Imagine walking into a bustling marketplace in a foreign country. The sights, sounds, and smells are overwhelming. You see vibrant textiles, intricate carvings, and tantalizing spices. You hear the rhythmic chatter of vendors and the melodic strains of traditional music. This sensory overload is a testament to the richness of the culture you’ve just encountered. But what exactly makes up this culture? Is it simply the things you see and hear, or is there something more intangible at play?
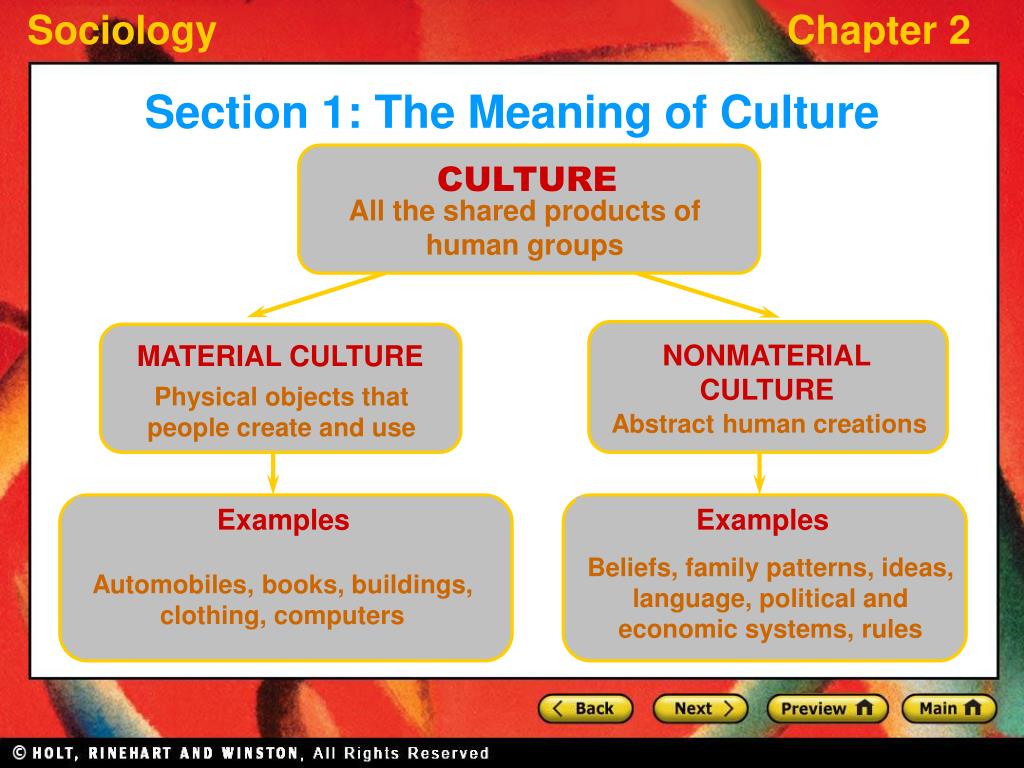
Image: www.slideserve.com
This is where the concepts of material culture and nonmaterial culture come into play. These two intertwined aspects define the essence of any culture, shaping the way individuals live, interact, and understand the world around them. Exploring their differences and connections offers a deeper understanding of human societies and their complexities.
Delving into Material Culture: The Tangible Expressions of Society
Material culture refers to the physical objects, artifacts, and technologies that are created and used by a society. These objects tell a powerful story about a culture’s values, beliefs, and practices. Everything from the clothes people wear and the houses they live in to the tools they use and the food they eat can be considered part of material culture.
Think about the iconic symbols of different cultures: the pyramids of ancient Egypt, the Taj Mahal in India, or the Eiffel Tower in France. These monumental structures are not only architectural marvels but also embodiments of the values, beliefs, and technological prowess of their respective societies. From everyday items like pottery and weaving techniques to grand monuments like temples and palaces, material culture provides tangible evidence of a culture’s history, traditions, and artistic expressions.
Understating Nonmaterial Culture: The Intangible Fabric of Society
While material culture is readily visible, nonmaterial culture encompasses the intangible aspects of a society. It includes ideas, values, beliefs, behaviors, customs, and norms that guide people’s interactions and shape their understanding of the world. This intangible realm is often referred to as the “culture of the mind” and is passed down through generations through language, education, and social interactions.
Think about the values of a culture like individualism, collectivism, or respect for elders. These concepts are not physical objects but are deeply embedded in a society’s identity and influence how individuals behave. Religious beliefs, traditions, and customs also fall under the umbrella of nonmaterial culture. For instance, celebrating certain holidays, observing religious practices, or adhering to social etiquette are all examples of nonmaterial cultural elements.
Nonmaterial culture profoundly impacts how individuals perceive and interact with their social environments. It sets social norms and expectations, shapes moral codes, and determines how people communicate and connect with each other. For example, a society’s nonmaterial culture dictates appropriate forms of address, acceptable behavior in public, and the values held sacred.
The Intertwined Relationship Between Material and Nonmaterial Culture
Material and nonmaterial culture are inextricably intertwined. The objects we create and use reflect our beliefs, values, and practices. For example, the tools used by a hunter-gatherer society reflect their nomadic lifestyle and dependence on nature, while the elaborate machinery used in a modern industrial society reflects its emphasis on technology and efficiency.
Conversely, nonmaterial culture influences how we create, use, and perceive material objects. For example, a society that values simplicity and sustainability might create minimalist furniture and prioritize reusable items, while a society that values status and wealth might value luxury brands and extravagant displays of possessions.
Understanding the interplay between material and nonmaterial culture is crucial for appreciating the complexities of human societies. It helps us to understand how societies evolve, adapt, and negotiate change over time. The objects we create and the values we hold are constantly interacting, shaping and being shaped by each other.

Image: www.tffn.net
Exploring Current Trends in Cultural Expression
The relationship between material and nonmaterial culture is constantly evolving as societies adapt to new technologies, global influences, and changing values. The explosion of digital technology has created new forms of material culture, such as smartphones, social media platforms, and virtual reality experiences. These technologies are not only reshaping how we communicate and consume information but also influencing our beliefs, values, and social interactions.
The rise of globalization has also led to greater cultural exchange and hybridization. We see a blurring of cultural boundaries as different cultures borrow from and influence each other. Food, fashion, music, and art are increasingly crossing borders, creating a rich tapestry of diverse cultural expressions.
These trends raise important questions about the role of material culture in shaping our identities and the impact of globalization on cultural values. As societies continue to evolve, it will be fascinating to observe how the interplay between material and nonmaterial culture continues to shape our world.
Expert Advice: Embracing Cultural Diversity
Understanding the differences between material and nonmaterial culture can enrich our lives and broaden our perspectives. Here are some tips for embracing cultural diversity:
- Travel and explore different cultures: Visiting new places and experiencing diverse cultures firsthand provides a powerful way to learn about different values, beliefs, and traditions.
- Be open-minded and respectful: When interacting with people from different backgrounds, it’s important to approach them with an open mind and respect their beliefs and customs, even if they differ from your own.
- Engage with diverse media and perspectives: Reading books, watching films, and listening to music from different cultures can help to expand your understanding of the world and foster empathy for other people.
- Challenge your own biases: Be willing to question your own assumptions and prejudices, and be open to learning from the experiences of others.
By actively engaging with cultural diversity, we can foster greater understanding, appreciation, and respect for the rich tapestry of human societies.
FAQs: Common Questions About Material and Nonmaterial Culture
Q: What are some examples of material culture?
A: Material culture encompasses the physical objects created and used by a society. Examples include:
- Tools and technologies: From simple tools like hammers and knives to complex machines like cars and computers.
- Clothing and adornment: The clothes people wear, their hairstyles, and jewelry.
- Housing and architecture: The types of houses, buildings, and infrastructure in a society.
- Art and crafts: Paintings, sculptures, pottery, textiles, and other forms of artistic expression.
- Food and cuisine: The ingredients, cooking methods, and meals that are characteristic of a culture.
Q: How does nonmaterial culture influence material culture?
A: Nonmaterial culture shapes how we create, use, and perceive material objects. For instance,:
- Religious beliefs: Religious practices and values might influence the design of temples and churches, the types of clothing worn, or the foods consumed during religious ceremonies.
- Social norms: Social expectations about appropriate behavior might influence the design of furniture or clothing styles.
- Values: A society that values sustainability might create products using recycled materials or prioritize fuel-efficient vehicles.
Q: How can I learn more about different cultures?
A: There are many ways to learn more about different cultures:
- Travel: Immerse yourself in different cultures by visiting new places and interacting with local people.
- Read books, articles, and blogs: Explore diverse cultures through the written word.
- Watch films and documentaries: Engage with diverse perspectives and stories through film.
- Listen to music: Explore the music of different cultures and discover new sounds and rhythms.
- Attend cultural events: Experience festivals, concerts, and exhibitions that celebrate cultural diversity.
By taking advantage of these resources, you can broaden your horizons and gain a deeper understanding of the world’s rich cultural tapestry.
What Is The Difference Between Material Culture And Nonmaterial Culture
Conclusion: A Deeper Appreciation of Cultural Nuances
Material and nonmaterial culture are two sides of the same coin, shaping the experiences and identities of societies. By understanding the differences and connections between them, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and richness of human cultures. As we navigate an increasingly interconnected world, embracing cultural diversity and understanding the interplay between material and nonmaterial expressions becomes essential for fostering empathy, respect, and a more inclusive global society.
Are you interested in learning more about the fascinating world of culture? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!





