Ever wondered why you might prefer a certain brand of clothing, or feel drawn to a particular group of people? The answer might lie in the invisible influence of reference groups – social groups that shape our values, beliefs, and behaviors. From the clothes we wear to the career paths we choose, reference groups play a crucial role in shaping our identities and influencing our decisions.

Image: www.researchgate.net
This article delves into the fascinating world of reference groups, exploring their impact on our lives and the complex ways they work in various social contexts. We’ll analyze different types of reference groups, examine their influence on consumer behavior, and discuss their implications for social mobility and identity formation. Understanding these powerful forces can provide valuable insights into our own choices and the dynamics of human interaction.
Defining Reference Groups: A Framework for Influence
In the realm of sociology, reference groups are defined as groups of individuals that serve as a point of comparison for an individual’s own attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors. These groups can provide a framework for understanding social norms, shaping our values, and influencing how we see ourselves in the world.
Think of reference groups as a set of mirrors reflecting back different aspects of ourselves. They can be both aspirational, guiding us towards desired goals, or negative, serving as a cautionary tale of what we don’t want to become. The influence of reference groups is not always conscious, often working subtly in the background to shape our choices and perceptions.
Types of Reference Groups: A Diverse Landscape of Influence
Reference groups can be categorized into various types, each exerting a unique influence on individual behavior. Understanding these categories can help us better comprehend the complex dynamics of social interaction:
1. Primary Reference Groups: The Foundation of Social Identity
Primary reference groups are characterized by close, intimate relationships, often formed within families, close friends, or immediate social circles. These groups wield significant influence on an individual’s values, beliefs, and sense of identity. They provide a bedrock of support, shape our moral compass, and often serve as the initial source of social learning.
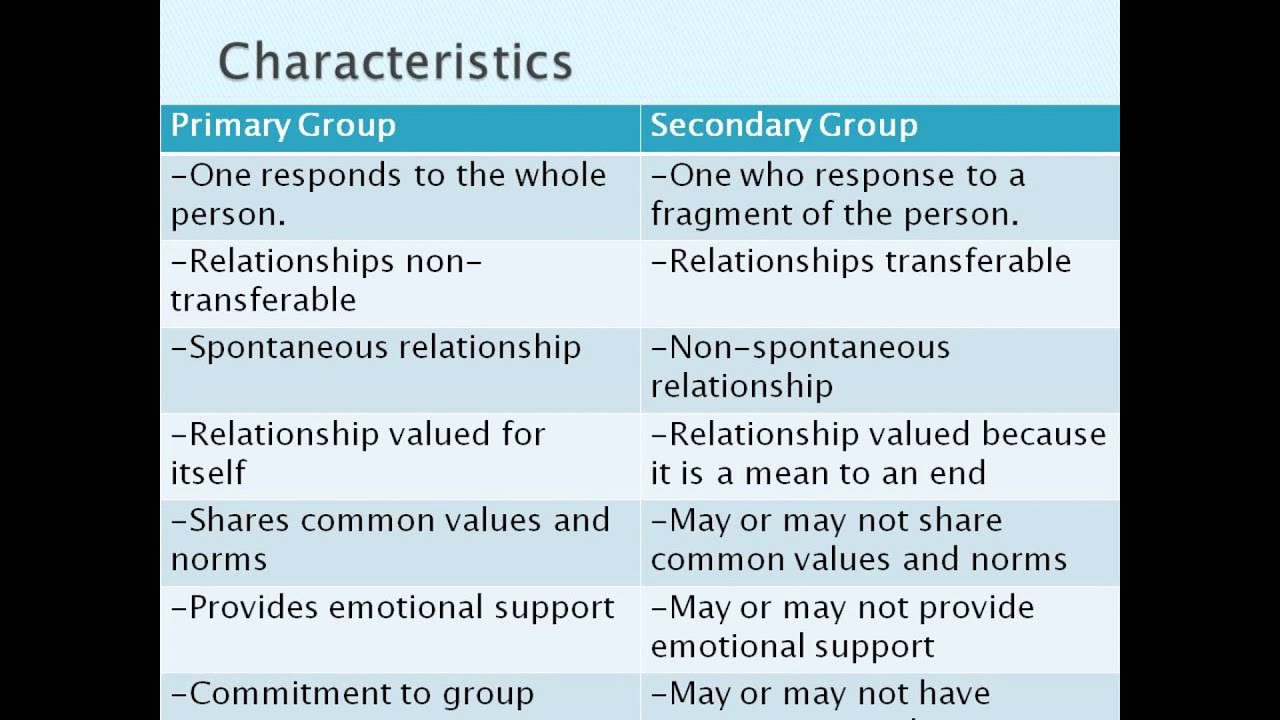
Image: www.youtube.com
2. Secondary Reference Groups: Expanding Our Social Horizons
Secondary reference groups are larger and more formal than primary groups, often based on shared interests, hobbies, or professional affiliations. These groups offer a broader perspective, exposing individuals to diverse ideas, viewpoints, and social norms. They can contribute to individual development, professional growth, and the expansion of social networks.
3. Aspirational Reference Groups: Reaching for Higher Ground
Aspirational reference groups represent individuals or groups that we admire and aspire to emulate. These groups embody desired qualities, lifestyle choices, or social positions. They can serve as a powerful motivator, inspiring us to strive for personal growth, achievement, and recognition.
4. Dissociative Reference Groups: Avoiding the Unwanted
Dissociative reference groups are groups that we actively distance ourselves from, often due to conflicting values, beliefs, or behaviors. They represent the antithesis of our own identities and aspirations, serving as a cautionary reminder of what we wish to avoid. These groups can fuel social and cultural divisions, highlighting the contrasting values and beliefs within a society.
Consumer Behavior: How Reference Groups Influence Our Choices
Reference groups play a crucial role in shaping consumer behavior, influencing our purchasing decisions, brand preferences, and overall spending habits. Here are some key ways reference groups impact our consumption patterns:
1. Informational Influence: Seeking Advice from Trusted Sources
Reference groups often serve as valuable sources of information about products and services. We rely on the opinions and experiences of those we trust, seeking out advice and recommendations for products that align with our needs and preferences. Whether it’s a friend recommending a new restaurant or a social media group offering tips on travel planning, informational influence plays a significant role in our decision-making process.
2. Normative Influence: Conforming to Social Expectations
Reference groups also exert normative influence, encouraging us to conform to social expectations and norms. We often purchase products or services not just for their functional benefits but also to align with the expectations of our social circles. For example, clothing choices are often influenced by what is deemed “fashionable” within a particular group, reflecting a desire to conform and be accepted.
3. Comparative Influence: Measuring Up to Social Norms
Reference groups also provide a framework for social comparison, allowing us to gauge our own status, possessions, and achievements relative to others. This comparative influence can motivate us to acquire goods or services deemed desirable within our reference groups, fueling a desire to “keep up with the Joneses” and maintain a certain level of social standing.
Social Mobility and Identity Formation: The Impact of Reference Groups
Beyond shaping our consumer choices, reference groups play a fundamental role in social mobility and identity formation. They can influence our aspirations, opportunities, and the paths we choose to pursue in life.
For example, individuals from low-income backgrounds may aspire to emulate higher-income reference groups, viewing their lifestyles and opportunities as desirable goals. This can motivate them to pursue education, professional development, and social advancement, striving to move up the socioeconomic ladder. However, it’s important to acknowledge that social mobility is complex and influenced by a multitude of factors, including systemic barriers and unequal opportunities.
Reference groups also contribute to the formation of our identity. The values, beliefs, and social norms we encounter within reference groups shape our sense of self, our perceptions of the world, and how we see ourselves fitting into society. These influences can be both positive and negative, guiding us towards personal growth or reinforcing existing biases and prejudices.
Reference Groups in the Digital Age: A Shifting Landscape
The rise of social media and the internet has fundamentally changed the landscape of reference groups. Online platforms connect individuals across geographic boundaries, creating vast networks of shared interests, values, and experiences.
Online communities, fan groups, and social media influencers can exert a powerful influence on individual beliefs and behaviors.
These digital reference groups, while providing opportunities for connection and shared experiences, also pose challenges in terms of information overload, misinformation, and the creation of echo chambers.
Reference Groups Examples Sociology
Conclusion: The Enduring Influence of Reference Groups
Reference groups remain a powerful force shaping our lives, dictating our choices, and influencing our identities. Understanding the diverse types of reference groups, their influence on consumer behavior, and their role in social mobility can provide valuable insights into the dynamics of human interaction. As social norms continue to evolve and the digital landscape expands, it’s essential to remain aware of the influence these groups exert and to critically evaluate the information and values they present.
The journey of self-discovery involves navigating the complex interplay of reference groups, embracing the positive influences, and challenging the negative. Ultimately, the choices we make and the identities we cultivate are shaped by the multifaceted world of reference groups, constantly influencing our perceptions and guiding our choices.





