Have you ever stopped to consider the invisible forces that shape your life? From the moment you wake up to the moment you lay your head down at night, you’re constantly interacting with social structures that guide your actions, shape your beliefs, and define your identity. These structures, known as social institutions, are the foundation upon which society is built. Today, we’ll delve into the world of primary social institutions, exploring how they impact our lives and the crucial role they play in shaping the world we know.

Image: jsu.edu
Primary social institutions are the fundamental building blocks of society, responsible for meeting basic human needs and fostering social order. These institutions are often deeply ingrained in our culture and history, influencing our values, beliefs, and behaviors from a young age. Understanding these institutions is essential for grasping the dynamics of society, recognizing the forces that shape our personal experiences, and appreciating the complexities of human interaction.
The Pillars of Society: Defining Primary Social Institutions
Primary social institutions are distinct from secondary institutions, which are more specialized and often emerge later in a society’s development. While secondary institutions like political parties, trade unions, and professional associations play vital roles, primary institutions are considered foundational, shaping the very fabric of society. They are often characterized by:
- Universality: They exist in all societies, albeit with variations in form and function.
- Permanence: They are enduring structures, persisting over generations.
- Influence: They exert a significant impact on the lives of individuals and the development of society.
The most widely recognized primary social institutions include:
- Family: The basic unit of society, responsible for procreation, socialization, emotional support, and the transmission of cultural values.
- Education: Institutions responsible for transmitting knowledge, skills, and values, preparing individuals for participation in society.
- Religion: Systems of beliefs and practices that provide meaning, values, and moral guidance, shaping individual behavior and social order.
- Economy: The system of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services, driving social progress and shaping power structures.
- Government: Institutions responsible for maintaining order, enforcing laws, and providing public services, ensuring the smooth functioning of society.
The Family: The Cradle of Society
The family, often described as the “foundation of society,” plays a vital role in the development of individuals and the perpetuation of cultural norms. It provides the initial social environment where children learn basic values, behaviors, and social skills. The family structure can vary greatly across cultures and time periods, from nuclear families to extended families, each with its unique dynamics and influences.
While traditional family structures have evolved significantly in recent decades, the family continues to be a primary source of social support, emotional security, and identity formation. It shapes individual perspectives on love, marriage, gender roles, and the meaning of family itself. The ongoing changes in family structures, including increased rates of single-parent households, blended families, and same-sex relationships, present new challenges and opportunities for understanding the evolving role of the family in modern society.
Education: Shaping Minds and Building Futures
Education is the institution responsible for transmitting knowledge, skills, and values to the next generation. It plays a crucial role in social mobility, preparing individuals for economic participation and active citizenship. Educational institutions, from early childhood programs to universities, foster intellectual development, critical thinking, and social skills, shaping individual perspectives and fostering social cohesion.
The evolution of education has mirrored societal changes, from traditional, rote learning to more hands-on, experiential approaches. Educational systems today face challenges of inclusivity, addressing diverse learning needs, and preparing students for an increasingly complex and rapidly evolving job market. The role of technology in education is also under constant scrutiny, as educators grapple with integrating digital tools while ensuring equitable access and ethical use.
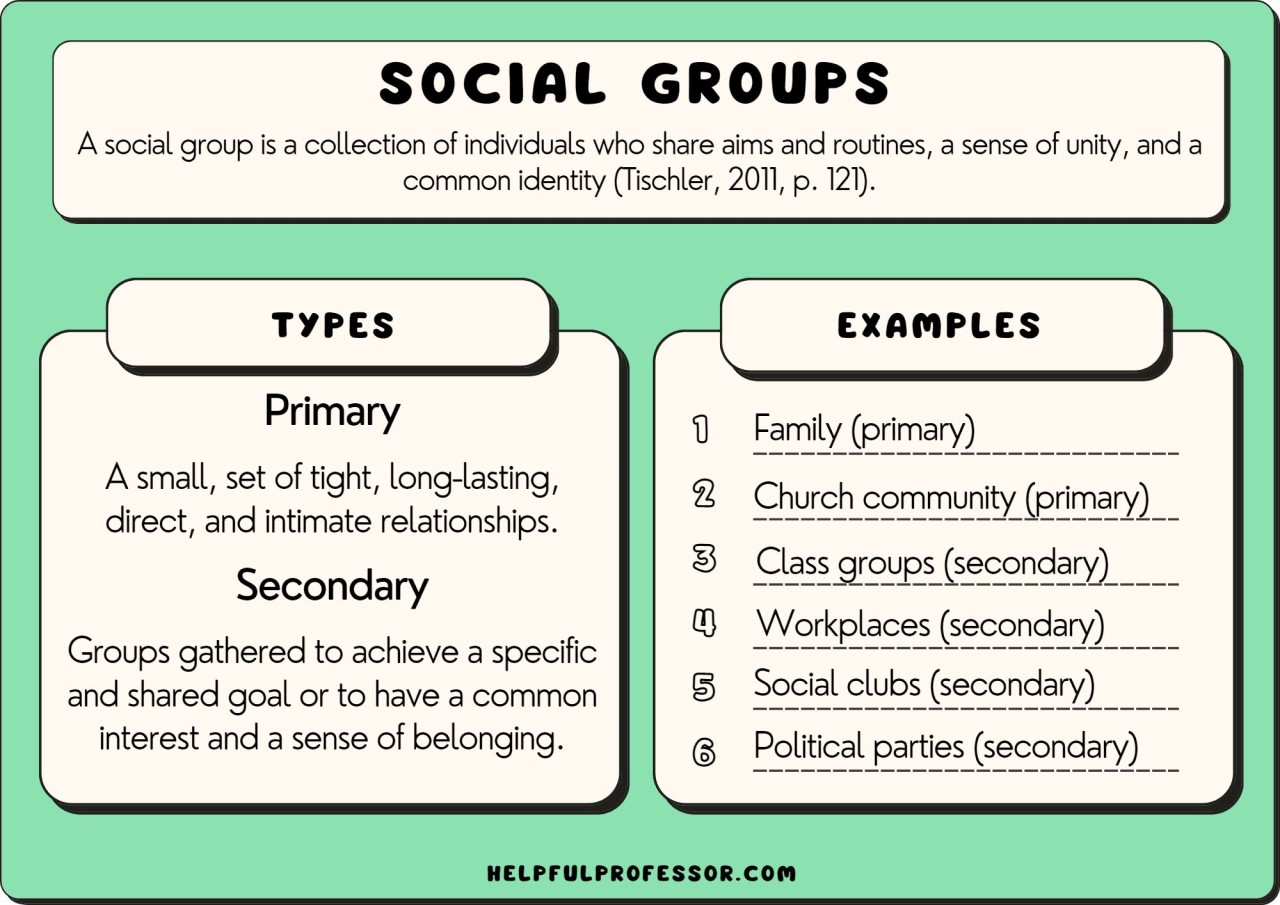
Image: helpfulprofessor.com
Religion: Guiding Beliefs and Moral Compass
Religion, as a system of beliefs and practices, offers individuals a framework for understanding the world, providing a sense of purpose, morality, and belonging. It shapes cultural norms, influences social behavior, and offers comfort and guidance during challenging times. Religious institutions like churches, temples, mosques, and synagogues serve as centers of worship and community, fostering social cohesion and providing opportunities for spiritual growth.
The influence of religion on society is multifaceted, impacting everything from art and architecture to laws and social policies. The role of religion in contemporary society is often debated, with some arguing for its continued relevance and others advocating for a separation of church and state. The ongoing discussions about faith, morality, and the role of religion in public life highlight the ongoing importance of understanding the complex relationship between religion and society.
The Economy: Driving Progress and Shaping Power
The economy, the system of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services, is the engine of societal progress. It drives innovation, creates employment, and fosters economic growth. The economy is shaped by multiple factors including government policies, technological advancements, and consumer demand. It also significantly influences power dynamics, with wealth and resources often concentrated in the hands of a few, while others struggle for economic security.
Understanding the economic system is crucial for comprehending the complexities of social inequality, the impact of global trade, and the forces that shape the lives of individuals and entire communities. The ongoing debates about economic justice, sustainable development, and the role of government in managing the economy reflect the importance of this primary social institution in shaping the modern world.
Government: The Framework for Order and Progress
Government, with its institutions like legislatures, courts, and administrative agencies, provides the framework for order and progress within society. It sets rules and regulations, enforces laws, and provides public services like education, healthcare, and infrastructure. The role of government varies across countries, ranging from minimalist states to more interventionist models.
The relationship between government and other primary social institutions is complex and often fraught with tension. Government policies can significantly impact the family, education, religion, and the economy. Conversely, these institutions can influence government policy through advocacy, lobbying, and public opinion. Understanding the interplay between these institutions is essential for grasping the political dynamics of a society and its evolution.
Understanding the Interconnectedness
Primary social institutions are not isolated entities; they are interconnected and mutually influence each other. The family shapes the values and beliefs transmitted through education, while education empowers individuals to participate more actively in the economy and government. Religious beliefs can influence economic decisions and government policies, while the economy can impact religious institutions through resource allocation and societal priorities.
These complex interrelationships create a dynamic system, constantly evolving in response to social, economic, and technological changes. Understanding these interconnections is crucial for addressing social problems, promoting social justice, and building a sustainable and equitable society.
Looking Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
Primary social institutions are facing a range of challenges in the 21st century. Rapid technological advancements, globalization, climate change, and increasing social inequality are presenting new demands and complexities for these institutions. From adapting educational systems to meet the needs of a digitally driven world to finding solutions to income inequality and climate change, primary institutions must evolve to address these challenges and meet the needs of a changing society.
Despite the challenges, there are also opportunities for positive change. Increased awareness of social issues, advancements in communication technology, and a growing global interconnectedness can foster collaboration and innovation in addressing societal issues. By strengthening primary social institutions, promoting social justice, and fostering inclusivity, we can work towards building a more just and equitable future for all.
Primary Social Institutions
Conclusion
Understanding primary social institutions is essential for navigating the complex world we live in. They provide the framework for our lives, shaping our identities, values, and behaviors. Recognizing the importance of these institutions, their interconnectedness, and the challenges they face empowers us to become more informed citizens, engage in meaningful discourse, and contribute to the creation of a more just and equitable society. We encourage you to continue exploring these topics, engage in dialogue with others, and seek ways to contribute to positive change within your own communities.





