Ever wondered why we go through years of schooling, memorizing facts and figures, and navigating complex curriculums? Beyond the obvious goal of acquiring knowledge, education holds a deeper set of purposes, often operating in the background, shaping our lives in ways we might not even realize. As a teacher, I’ve witnessed firsthand the transformative power of education, but it’s the less obvious impacts that truly fascinate me. Today, we embark on a journey to explore the manifest and latent functions of education, unraveling the hidden forces that influence our society and individuals.

Image: www.slideshare.net
Imagine a bustling classroom filled with eager students, intently listening to their teacher, absorbing new information, and engaging in lively discussions. On the surface, it appears to be a simple scene of learning and knowledge transfer. However, beneath this apparent simplicity lies a complex tapestry of intended and unintended consequences, forming the foundation of what we term the manifest and latent functions of education. The term “function” in this context refers to the intended or unintended consequences of a social institution, in this case, education.
Deciphering the Functions of Education
Manifest Functions: The Explicit Goals
Manifest functions are the readily apparent, intended goals of education. These are the explicit purposes that society recognizes and promotes. Think of them as the visible gears of a machine, actively working towards a specific outcome. Common manifest functions of education include:
- Knowledge and Skill Acquisition: Education aims to equip individuals with the knowledge, skills, and critical thinking abilities necessary to function effectively in society.
- Career Preparation: Schools prepare students for future careers, providing the knowledge and skills required for specific professions.
- Socialization: Education plays a crucial role in socializing individuals into societal norms, values, and expectations, fostering a sense of belonging and shared identity.
- Personal Growth and Development: Education promotes individual growth and development, helping students discover their passions, interests, and talents while shaping their values and worldview.
- Civic Engagement: Education empowers individuals to become active and informed citizens, fostering their understanding of societal issues and encouraging their participation in democratic processes.
These manifest functions are the driving forces behind educational systems globally, representing the explicit goals that educators, policymakers, and society at large strive to achieve.
Latent Functions: The Unseen Influences
Latent functions, on the other hand, are the unintended consequences of education, often hidden beneath the surface but nevertheless shaping individuals and society. They are the subtle forces, like the hidden currents beneath the ocean, that influence us without our conscious awareness. Here are some key latent functions of education:
- Social Control: Education serves as a tool for social control, promoting obedience, conformity, and compliance with societal norms and values. Schools enforce rules, instill discipline, and encourage adherence to expectations, helping maintain social order.
- Social Placement: Education plays a critical role in social placement, sorting individuals into various social strata based on their academic performance and social background. This process can lead to inequalities in opportunity, access to resources, and social mobility.
- Cultural Transmission: Education instils cultural values, beliefs, and traditions, transmitting them from one generation to the next. Through curriculum, textbooks, and social interactions within the educational environment, students learn about their culture, history, and shared heritage.
- Networking and Social Capital: Educational institutions provide opportunities for individuals to develop social connections, build relationships, and create networks. These networks can be beneficial for future career advancement, access to resources, and social support.
- Delayed Entry into the Workforce: Education can function as a mechanism for delaying entry into the workforce, providing individuals with extended periods of learning and development before assuming adult roles and responsibilities. This can have both positive and negative consequences, depending on the specific context.
While these latent functions may not be explicitly intended, their impact on individuals and society is profound and undeniable.
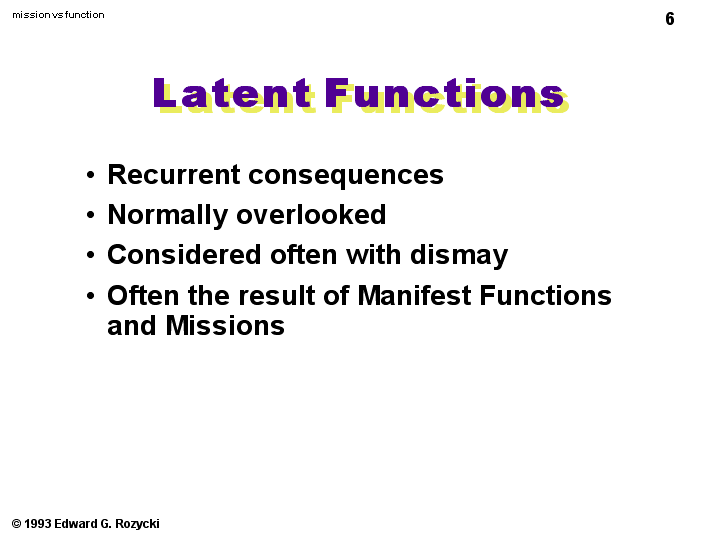
Image: www.newfoundations.com
The Evolving Landscape of Education
The realm of education is constantly evolving, influenced by technological advancements, societal shifts, and global trends. The rise of online learning, personalized learning platforms, and digital tools has significantly impacted the delivery and content of education. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) fields has prompted changes in curriculum design and resources. The focus on 21st-century skills, such as problem-solving, critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity, has led to a shift in pedagogical approaches.
The world is becoming increasingly interconnected and complex, demanding a new generation of individuals equipped with the skills and knowledge to navigate a rapidly changing environment. In response to these challenges, educators and policymakers are exploring innovative approaches, incorporating technology, promoting global citizenship, and fostering creativity and critical thinking. This evolving landscape presents both opportunities and challenges for education to fulfill its manifest and latent functions effectively.
Tips and Expert Advice for Navigating the Functions of Education
Understanding the manifest and latent functions of education can provide individuals with valuable insights into the educational landscape, enabling them to make informed decisions about their learning journey and approach to education. Here are some tips and expert advice to help you navigate the complex world of education:
- Be Proactive: Don’t passively accept the curriculum and learning environment. Actively seek out opportunities to explore your interests, develop skills, and engage in meaningful learning experiences.
- Critical Thinking: Don’t just absorb information passively. Question, analyze, and evaluate the knowledge and perspectives you encounter. Develop your own critical thinking skills to determine the validity and relevance of the information presented.
- Network and Connect: Leverage the educational environment to build valuable connections and relationships with teachers, peers, and mentors. These connections can provide support, guidance, and opportunities for future growth.
- Embrace Challenge: Don’t shy away from challenging courses or subjects. Push yourself outside of your comfort zone to expand your knowledge, skills, and perspectives.
- Reflect and Adapt: Continuously reflect on your learning journey, identifying areas for improvement and adapting your approach as needed. Stay open to new ideas and perspectives, recognizing that education is a lifelong process.
By actively engaging in your education, developing critical thinking skills, building relationships, embracing challenges, and reflecting on your learning process, you can maximize the benefits of education, achieving your desired outcomes while navigating the influence of both manifest and latent functions.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between manifest and latent functions?
A: Manifest functions are the intended and explicit consequences of education, such as knowledge acquisition and career preparation. Latent functions, on the other hand, are the unintended and often hidden consequences, such as socialization and social control.
Q: How can I identify the latent functions of my own education?
A: Reflect on your experiences in school, considering the subtle impacts beyond the explicit curriculum. For example, think about how your interactions with peers, teachers, and school environment have shaped your values, beliefs, and social skills.
Q: How can education be used to promote social equality?
A: Education can play a critical role in promoting social equality by providing equal opportunities for all individuals, regardless of their background or social status. This requires addressing systemic inequalities and ensuring equitable access to quality education.
Q: Should we focus more on manifest or latent functions in education?
A: Both manifest and latent functions are important. While promoting intended goals such as knowledge acquisition is crucial, recognizing and addressing unintended consequences is equally vital to ensure a more equitable and inclusive educational system.
Manifest And Latent Functions Of Education
https://youtube.com/watch?v=LcluY6UsVXY
Conclusion
The journey into the realm of manifest and latent functions reveals the intricate interplay of intended and unintended consequences in shaping the educational experience. Understanding these functions allows us to gain a deeper appreciation for the profound influence of education on individuals and society. By embracing critical thinking, seeking out opportunities for growth, and recognizing both the intended and unintended impacts of education, we can empower ourselves to navigate the educational landscape effectively and contribute to a more just and equitable future.
Are you interested in exploring the manifest and latent functions of education further? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.





