Imagine walking into a crowded cafe. You see people laughing, talking, and working on their laptops. But what are they actually experiencing? What are their individual stories, their hopes, and the meanings they attach to this simple act of being in a cafe? This is where interpretivism comes in. It’s not just about observing the outward behavior but delving deeper into the subjective world of human experience, understanding the motivations, beliefs, and interpretations that shape our actions.

Image: www.slideshare.net
Interpretivism is a philosophical approach that emphasizes the importance of understanding human behavior through the lens of meaning. It’s about recognizing that our actions aren’t just reactions to external stimuli but are guided by our internal world of thoughts, feelings, and interpretations.
The Heart of Interpretivism
Understanding Human Action
Interpretivism challenges the purely objective, scientific view of social research. It suggests that social reality isn’t something fixed and measurable, but rather a constantly evolving interpretation. Instead of looking for universal laws that govern human behavior, interpretivists believe that we need to understand the meanings that people attribute to their actions. It’s about getting inside the heads of individuals, so to speak, to grasp the subjective experience that shapes their behavior.
Qualitative Methods
Interpretivism leans heavily on qualitative research methods. Instead of numbers and measurements, it utilizes interviews, observations, and textual analysis to collect rich data on people’s experiences, perceptions, and interpretations. These methods allow researchers to dig deeper into the nuances of human behavior and uncover the often-unseen layers of meaning that underlie our actions.
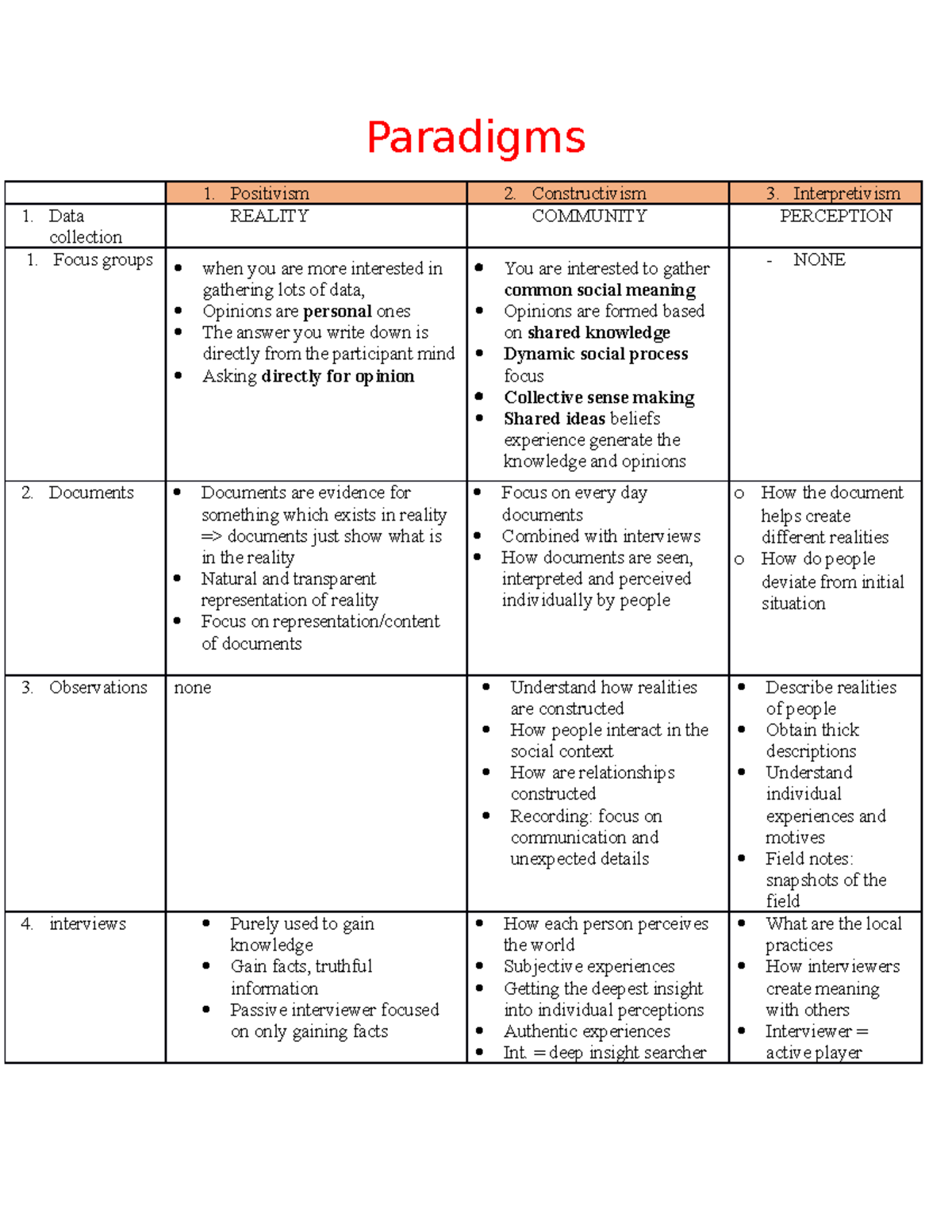
Image: www.studocu.com
The Importance of Context
Interpretivism emphasizes the role of context. It recognizes that human behavior can’t be understood in isolation. We are all products of our social environments, our cultural backgrounds, and our individual histories. These factors shape our perspectives, values, and interpretations of the world around us. Interpretivist research therefore seeks to understand the specific context in which actions take place, recognizing that the same action might have different meanings in different settings.
Key Thinkers in Interpretivism
Interpretivism draws inspiration from a diverse range of thinkers who have challenged traditional, positivist approaches to understanding reality. Some key figures include:
- Max Weber: Known for his work on verstehen (understanding), emphasizing the importance of understanding the subjective meanings people attach to their actions.
- Alfred Schutz: Focused on the “lifeworld,” the taken-for-granted world of everyday experience, and how people make sense of their surroundings through shared understandings.
- Clifford Geertz: Emphasized the cultural and symbolic dimensions of social life, arguing that meaning is embedded in the rituals, symbols, and narratives of a community.
The Impact of Interpretivism
Interpretivism has had a profound impact on social sciences like anthropology, sociology, and psychology. It has challenged the traditional focus on objective measurements and opened up new pathways for understanding the complexities of human experience. Think of anthropology’s use of participant observation to immerse in a culture, or sociology’s use of in-depth interviews to explore people’s lived experiences.
Current Trends in Interpretivism
Interpretivism continues to evolve, incorporating new approaches and responding to emerging challenges in the social world. Today, there is growing interest in:
Digital Ethnography
With the rise of digital platforms, researchers are leveraging online spaces to conduct ethnographic studies. By analyzing online communities, social media interactions, and digital artifacts, they gain insights into how people construct meanings and interact online.
Postmodern Interpretivism
This approach emphasizes the fragmented and fluid nature of meaning in a postmodern world. It acknowledges the power dynamics, social structures, and cultural narratives that shape our interpretations and argues that truth is not a singular, objective entity but rather a multitude of perspectives.
Critical Interpretivism
This branch of interpretivism focuses on analyzing power relations and challenging dominant narratives. It draws on critical theory to examine how social structures, ideologies, and discourses shape our understanding of the world, leading to power imbalances and inequalities.
Tips for Applying Interpretivism
Whether you’re a researcher or simply trying to better understand the world around you, interpretivism offers valuable insights. Here are some tips for applying its principles:
Emphasize Context
Remember that actions can’t be understood in isolation. Take into account the cultural, social, and historical context in which they occur. Think of how a person’s behavior might be influenced by their family background, their political views, or their experiences in their community.
Seek Diverse Perspectives
Don’t rely on a single perspective. Seek out different voices, experiences, and interpretations. This can involve engaging with people from diverse backgrounds, reading multiple accounts of the same event, and reflecting on your own biases and assumptions.
Engage in Active Listening
When interacting with others, practice active listening. Pay attention to both the content of what people say and the way they say it. Observe their body language, their tone of voice, and the emotions they express. This can help you understand the underlying meanings and interpretations they are conveying.
FAQ
Q: What are some examples of interpretivist research?
A: There are countless examples! Think of ethnographic studies of indigenous cultures, interviews with refugees to understand their experiences, or textual analysis of literature to explore themes of identity and social change. These studies all seek to understand the subjective meanings and interpretations that shape human behavior.
Q: What are the limitations of interpretivism?
A: While interpretivism offers valuable insights, it’s not without limitations. Some critics argue that it can be subjective, relying heavily on the researcher’s interpretation, and that it might not be generalizable to other contexts. Additionally, some argue that its focus on individual meaning can overlook the role of structural factors in shaping behavior.
Q: How can I learn more about interpretivism?
A: A great place to start is by exploring the work of key thinkers like Max Weber, Alfred Schutz, and Clifford Geertz. You can also find introductory texts on interpretivism in social science or qualitative research methods. Engage with online forums and academic journals to stay updated on current trends and debates.
What Is Interpretivism
Conclusion
Interpretivism offers a powerful lens for understanding the complexities of human experience. By recognizing the role of meaning, context, and subjectivity, we can gain a richer understanding of individuals, societies, and the world around us.
Are you interested in learning more about interpretivism? Share your thoughts and questions below, and let’s continue the conversation!





