Imagine a bustling city, filled with diverse individuals each with their own goals and motivations. Yet, despite this apparent chaos, the city functions. Traffic flows smoothly, businesses operate, and communities thrive. How is this possible? How do seemingly disparate parts come together to create a functioning whole? This is where the sociological perspective of structural functionalism, pioneered by Émile Durkheim, comes into play. Like a skilled architect, Durkheim challenged us to see society as a complex, interconnected system, where each part contributes to its stability and survival.
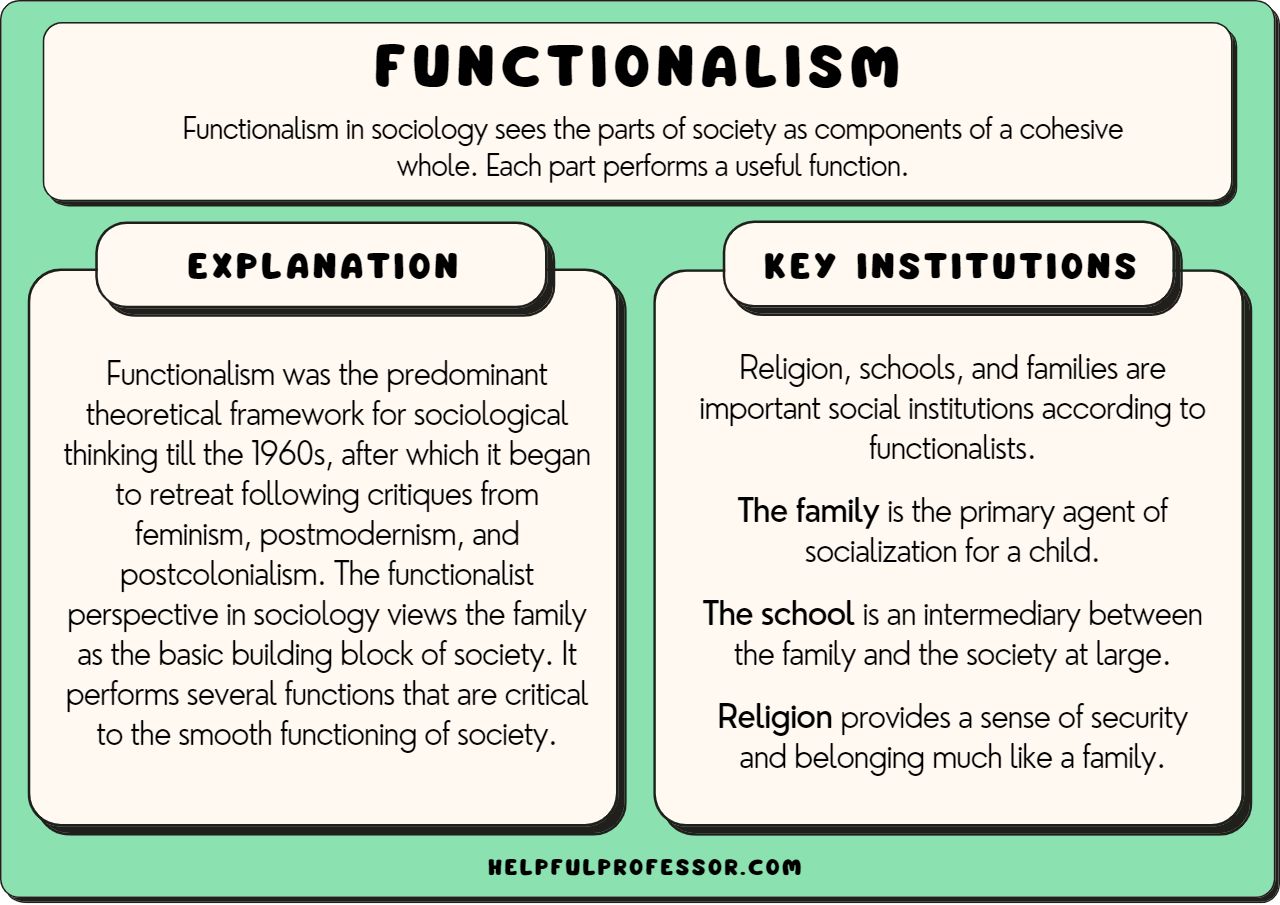
Image: ar.inspiredpencil.com
Durkheim’s work wasn’t just an academic exercise; it was a response to the rapid social changes of the 19th century. The Industrial Revolution, urbanization, and the rise of individualism were shaking the foundations of traditional societies. He sought to understand how societies could maintain order and cohesion in the face of these seismic shifts, proposing that social structures, like the organs of a body, each play a vital role in keeping the whole functioning.
The Core Principles of Structural Functionalism
Structural functionalism, also known as functionalism, views society as a complex system with interrelated parts that work together to maintain stability and order. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of social structures and institutions, arguing that each element serves a specific function, contributing to the overall equilibrium of society. Think of it as a delicate ecosystem where each organism plays a vital role, contributing to the overall balance and survival of the system.
Key tenets of structural functionalism include:
- Social solidarity: Durkheim emphasized the importance of shared values, beliefs, and norms in creating and maintaining social cohesion. This sense of belonging helps individuals to feel connected to society and contribute to its well-being.
- Functional interdependence: Social institutions, from the family to the government, are seen as interdependent, with each playing a crucial role in sustaining the whole. The breakdown of one institution can have ripple effects across the entire social system, impacting the stability and functionality of society.
- Equilibrium and stability: Structural functionalism emphasizes the importance of social stability and order. It argues that societies tend to seek equilibrium, with disruptive forces met by mechanisms that restore balance. For instance, social movements or protests might challenge existing power structures, but the system adapts and adjusts to re-establish a new equilibrium.
Emile Durkheim: A Pioneer of Structural Functionalism
Emile Durkheim, a French sociologist, played a pivotal role in shaping the field of sociology and laying the foundation for structural functionalism. Born in 1858, he grappled with the social changes of his time and aimed to understand how societies could maintain order and cohesion. He believed that sociology should focus on studying social facts, or the social patterns and structures that influence individual behavior.
Durkheim’s landmark work, “The Division of Labor in Society,” published in 1893, explored how the increasing specialization of labor in modern societies could lead to new forms of social solidarity. He argued that in traditional societies, mechanical solidarity, based on shared values and beliefs, held communities together. In contrast, modern industrial societies were characterized by organic solidarity, where interdependence and shared needs bound individuals together.
Another significant contribution was his analysis of suicide in “Suicide” (1897). Durkheim demonstrated that suicide rates were influenced by social factors, not merely individual psychological states. He identified different types of suicide, including egoistic (low social integration), altruistic (high social integration), anomic (lack of social regulation), and fatalistic (excessive social regulation).
The Strengths and Limitations of Structural Functionalism
Structural functionalism has been influential in sociological thought, offering a framework for understanding the complex interplay of social structures and institutions. It highlights the importance of social order, shared values, and the harmonious functioning of society. However, it also faces criticism for its inherent conservatism and lack of focus on social inequality and conflict.
Critics argue that structural functionalism:
- Overlooks power dynamics: It tends to downplay the role of power structures and social inequalities, focusing instead on the harmonious functioning of society. This perspective can overlook the ways in which social structures disadvantage certain groups.
- Preserves the status quo: Its emphasis on stability and order can be seen as conservative, implying that change is disruptive and potentially harmful to social equilibrium. This can lead to resistance to social reform or addressing systemic issues.
- Lacks agency: It focuses primarily on the influence of social structures on individuals, neglecting the capacity of individuals to challenge or change those structures.

Image: momentumclubs.org
Modern Applications and Criticisms
Structural functionalism, although criticized, remains relevant in understanding how societies function. It provides useful insights into the role of institutions, cultural norms, and shared values in shaping social behavior. For example, it helps explain the importance of education in socializing future generations, the role of the family in transmitting values, and the vital role of the government in maintaining law and order.
However, modern sociologists have moved beyond a strict functionalist perspective, incorporating ideas from other schools of thought, such as conflict theory and symbolic interactionism. These perspectives acknowledge the dynamics of power and conflict, as well as the role of human agency in shaping social reality.
Tips for Applying Structural Functionalism to Your Understanding of Society
Think of society as a puzzle, where each piece plays a crucial role in creating the complete picture. Consider the following tips for applying a functionalist lens to your observations of society:
- Identify the key institutions: Observe the various institutions in your community, such as the family, education, religion, the economy, and the government. Consider how they are interconnected and how they contribute to the overall functioning of society.
- Analyze shared values and norms: Examine the dominant cultural values and norms that shape behavior in your community. How do these contribute to social cohesion and stability? Look for instances where these values conflict or are challenged.
- Explore social change and adaptation: Don’t just focus on stability. Observe how societies adapt to change and evolve. Think about how new social movements or technological advancements might be shaping existing institutions or norms.
FAQs about Durkheim and Structural Functionalism
Q: What are the main critiques of structural functionalism?
A: Critics argue that structural functionalism oversimplifies social dynamics by ignoring power imbalances, conflict, and the agency of individuals. These are crucial aspects of understanding society.
Q: How does structural functionalism differ from other sociological perspectives like conflict theory?
A: While structural functionalism focuses on stability and consensus, conflict theory emphasizes power struggles, social inequality, and the potential for social change driven by conflict between groups with differing interests.
Q: Is structural functionalism still relevant today?
A: Although it has limitations, structural functionalism can still provide helpful insights into the workings of institutions and the influence of shared cultural values. However, it needs to be combined with other perspectives to offer a more nuanced understanding of complex social phenomena.
Emile Durkheim Structural Functionalism
Conclusion: Understanding the Building Blocks of Society
Emile Durkheim’s structural functionalism provides a valuable lens through which to understand how societies operate, focusing on the contributions of various social institutions and shared values to maintaining social order and equilibrium. While it has limitations, especially in a modern world marked by complex inequalities and social change, it remains a cornerstone of sociological analysis.
We encourage you to continue exploring Emile Durkheim’s work and delve deeper into the fascinating world of structural functionalism. Are you interested in learning more about this perspective, or perhaps exploring how it intersects with other sociological theories? Let us know in the comments below!





