Imagine a young child, barely able to speak, sitting at a table with their family. They pick up a spoon and, with a determined expression, try to feed themselves. The parents, beaming, guide their hand, showing them how to scoop the food and bring it to their mouth. This seemingly routine act is a prime example of socialization, a process where individuals learn the norms, values, and beliefs of their society, and the parents in this scenario are agents of socialization. From the moment we are born, we are constantly learning and adapting to the world around us. Our families, schools, peers, the media, and even the workplace become the conduits through which we absorb the rules and expectations that shape who we are.
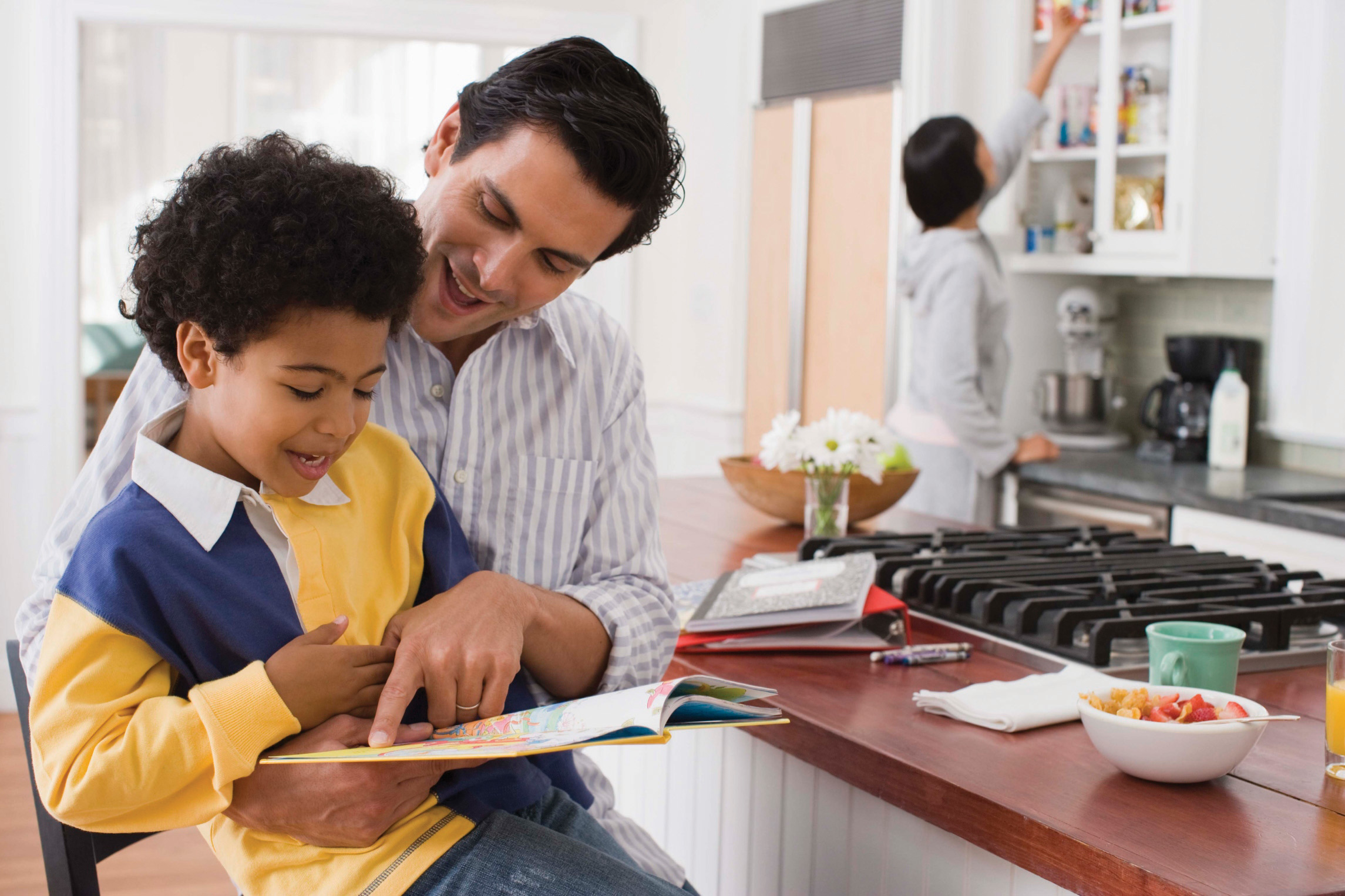

Image: flatworldknowledge.lardbucket.org
This article delves into the fascinating world of agents of socialization. We will explore what they are, how they influence us, and the ever-evolving dynamics of this crucial process. Prepare to gain a deeper understanding of the intricate forces that contribute to the development of individuals and shape the very fabric of our society.
Agents of Socialization: The Architects of Our Social Selves
To grasp the concept of agents of socialization, we must first understand the concept of socialization itself. Socialization is the lifelong process through which individuals learn the knowledge, skills, values, beliefs, and behaviors necessary to function effectively in society. It is the way we acquire the cultural and social frameworks that allow us to interact with others, understand the world around us, and navigate its complexities.
Family: The First and Foremost Socialization Hub
The family is often considered the primary agent of socialization. It is within the family that children first learn language, develop basic social skills, and internalize fundamental values. Parents, siblings, and extended family members play crucial roles in teaching children how to behave, what to believe, and what is considered right or wrong. This foundational learning shapes how children see themselves and their place in the world.
School: A Microcosm of Society
Schools are another powerful agent of socialization. They provide a structured environment where children learn not only academic knowledge but also social norms. Teachers, administrators, and classmates all contribute to shaping a child’s beliefs and behaviors. The school environment teaches children to follow rules, collaborate with others, and develop problem-solving skills. It broadens their social horizons and exposes them to diverse perspectives.
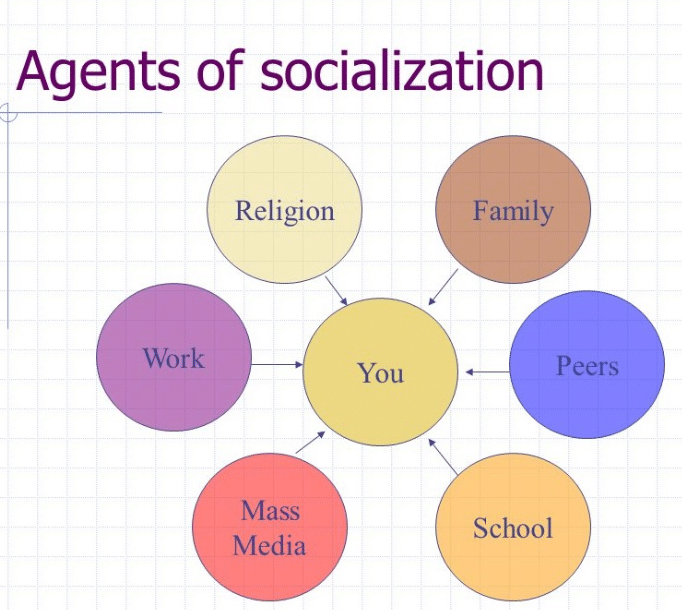
Image: amazonia.fiocruz.br
Peers: Building Relationships and Defining Identity
Peer groups are essential agents of socialization, especially during adolescence and young adulthood. Peers provide an opportunity for young people to develop independence, test boundaries, and experiment with different identities. Social interactions with friends and peers shape individuals’ values, beliefs, and behaviors, and they often play a role in shaping an individual’s self-esteem and sense of belonging. Peer pressure, the influence exerted by one’s peers to conform to group norms, can have a powerful impact on individuals’ decision-making and behaviors.
Media: Weaving Narratives and Shaping Perceptions
The media, encompassing television, movies, music, and digital platforms, is a pervasive and influential agent of socialization. It shapes our perceptions of the world, influencing our values, beliefs, and behaviors. The media can portray stereotypes, promote consumerism, and influence political attitudes. It can also expose us to new ideas and cultures, broadening our horizons and fostering understanding. The impact of media on socialization is a complex and multifaceted topic that deserves further exploration.
Workplace: Navigating the Professional World
The workplace is another important agent of socialization, especially for adults. It is here that individuals learn professional skills, build relationships with colleagues, and adapt to the norms of corporate culture. Workplace socialization involves understanding the unwritten rules, expectations, and values associated with particular professions. It can influence individuals’ career paths, their sense of self-worth, and their overall well-being.
Emerging Trends in Socialization: The Digital Age and Beyond
In the age of digital interconnectedness, the landscape of socialization is undergoing a rapid transformation. New technologies and social media platforms have significantly impacted how we learn, interact, and form identities. The rise of social media has created new virtual spaces where individuals connect, share information, and develop their identities. These platforms can both enhance and complicate the process of socialization, providing unprecedented opportunities for connection and learning while also posing challenges related to privacy, safety, and the formation of accurate perceptions.
Socialization in a Globalized World
Globalization has also contributed to the global interconnectedness of cultures and has led to increased exposure to diverse perspectives. This has created complex dynamics in socialization, as individuals navigate a world where multiple cultures and values intersect. This globalized environment requires individuals to develop a greater understanding of different cultures and how to interact with people from diverse backgrounds.
Expert Tips for Navigating the Socialization Process
Socialization is an ongoing process that begins at birth and continues throughout our lives. We are constantly learning and adapting to the social world around us. Here are some tips to help you navigate this complex process effectively and cultivate healthy relationships:
Be Open to New Experiences
Embrace the opportunity to learn from different cultures, perspectives, and ways of life. Engage with people from diverse backgrounds, explore new interests, and step outside your comfort zone. This can broaden your horizons, challenge your preconceived notions, and foster empathy and understanding.
Develop Critical Thinking Skills
Learn to question assumptions, analyze information, and form your own opinions. Be aware of the biases and influences that shape your perceptions. Be critical of the information you consume, particularly in the digital age, where misinformation is widespread. Cultivating critical thinking skills enables you to navigate the complexities of the social world with greater awareness and discernment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the key differences between primary and secondary socialization?
A: Primary socialization refers to the initial stages of socialization, primarily through the family and immediate community. Secondary socialization occurs later in life, through institutions such as school, the workplace, and peer groups. It is characterized by more formal learning and a broader range of social interactions.
Q: How does technology impact socialization?
A: Technology, particularly social media, has both positive and negative effects on socialization. It provides platforms for connection, shared experiences, and the formation of online communities. However, it can also lead to social isolation, cyberbullying, and the development of unrealistic expectations and comparisons.
Q: Are there any negative aspects to socialization?
A: While socialization is essential for social integration and functioning, it can also be a source of conformity, peer pressure, and the internalization of harmful norms and values.
What Is Agent Of Socialization
Conclusion
Understanding agents of socialization is crucial for recognizing how we develop into social beings. From the family to the workplace, these forces shape our values, beliefs, and behaviors. As the world continues to evolve, the dynamics of socialization are constantly shifting. Adapting to these changes and embracing a lifelong learning approach are key to navigating the complexities of the social world. Are you interested in exploring specific examples of how agents of socialization influence individuals’ lives? Share your thoughts in the comments below!





