Imagine walking into a room full of people and instantly knowing where you stand in the social hierarchy. You might feel a sense of comfort and belonging if you recognize familiar faces and shared experiences. Alternatively, you might feel a sense of discomfort or isolation if you feel different or out of place. These seemingly automatic social judgments are shaped by the concepts of ascribed and achieved status, two fundamental pillars of social stratification.

Image: gbu-taganskij.ru
The concept of status can be intimidating, but it’s a key to understanding how we navigate social interactions. It represents our position within a social group, influenced by factors like wealth, education, occupation, and family background. While we often associate status with individual achievement, the reality is far more complex. This article will delve into the fascinating world of ascribed and achieved status, exploring their nuances and providing real-life examples to illustrate their impact on our social lives.
Unpacking Ascribed and Achieved Status
Ascribed status is the social position we are born into and essentially given to us. It’s the status we have no control over, determined by factors beyond our choices. Think of it like the starting point in a game, where factors like race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, family background, and caste (in some cultures) play a significant role in shaping our initial social positioning.
Achieved status, on the other hand, is the social position we earn through our efforts and choices. This is the dynamic part of our social identity, where education, occupation, wealth, and individual accomplishments shape our standing in society. It’s like the journey in a game, where individual actions determine our progress and position within the social landscape.
Ascribed Status: The Unchosen Trajectory
Ascribed status plays a powerful role in shaping our experiences and opportunities, even before we begin to make our own choices. For example, a child born into a wealthy family might be provided with access to elite education, healthcare, and social networks, potentially setting the stage for a successful and privileged life. Conversely, a child born into poverty might face limited opportunities for education and healthcare, potentially creating a cycle of hardship and disadvantage.
Achieved Status: The Path of Choice and Effort
Achieved status recognizes individual effort and accomplishments, allowing individuals to shape their own destinies. A person with a strong work ethic and dedication to education could potentially rise from humble beginnings to a position of leadership and influence. However, even achieved status can be influenced by ascribed status, as structural inequalities can create barriers to opportunity and upward mobility.
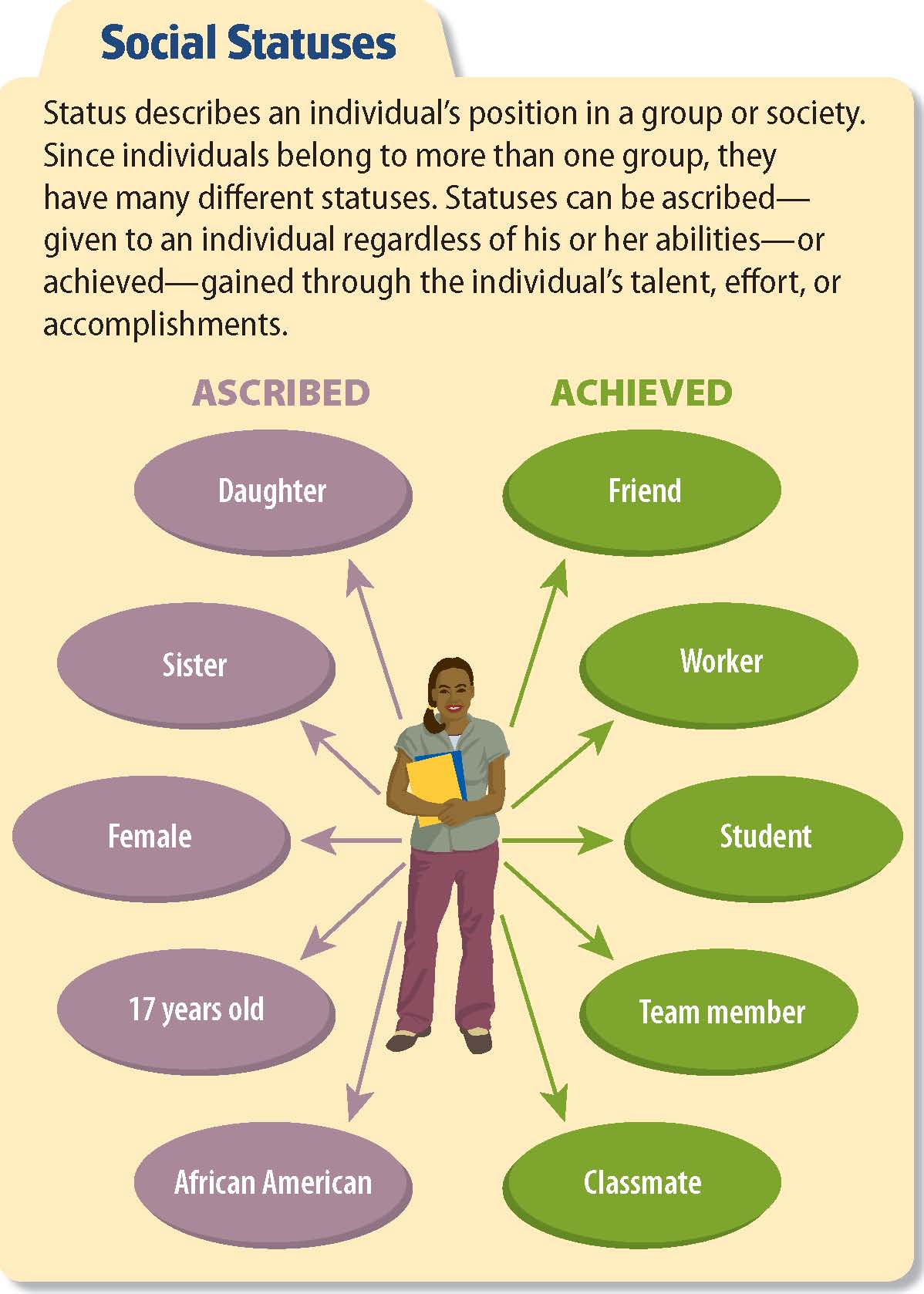
Image: readingandwritingprojectcom.web.fc2.com
The Interplay of Ascribed and Achieved Status
The reality of social stratification often lies in the complex interplay between ascribed and achieved status. While our initial position might be influenced by factors beyond our control, individual choices and efforts can create opportunities for upward mobility. The journey from ascribed status to achieved status can be challenging, particularly for those facing significant social disadvantages. It often requires resilience, determination, and a willingness to break down systemic barriers.
For instance, a woman born into a family with limited resources might face significant challenges in accessing higher education. However, through sheer perseverance and dedication, she might be able to attain a university degree, opening doors to a more prosperous and fulfilling life. This achievement highlights how individual efforts can overcome limitations imposed by ascribed status.
Exploring Real-World Examples
Ascribed Status:
- Royal Family Members: Individuals born into a royal family automatically inherit a position of power and privilege, determined by their lineage rather than their individual accomplishments.
- Castes in India: The caste system in India assigns individuals to specific social categories based on their birth, with associated rights, responsibilities, and limitations.
- Gender and Race: Societal expectations and opportunities can vary significantly based on gender and race, reflecting the impact of ascribed status on individual experiences.
Achieved Status:
- Doctors and Engineers: Individuals who invest years in education and training to attain professional qualifications achieve a higher social standing.
- Entrepreneurs: Successful entrepreneurs build their own businesses and amass wealth, earning a prestigious social status through their achievements.
- Athletes and Artists: Individuals who excel in their chosen fields, demonstrating exceptional skills and talent, gain recognition and social acclaim.
Navigating the Dynamics of Ascribed and Achieved Status
The concept of ascribed and achieved status is not simply an academic exercise. It impacts how we view ourselves and others, how we interact, and how we perceive the world. Understanding these dynamics can empower us to be more sensitive and aware of the diverse experiences of people around us.
Expert Advice and Tips
While we might not be able to directly change our ascribed status, we can foster a more equitable society by understanding and addressing the systemic inequalities that influence individual opportunities.
Here are some actionable tips to cultivate a more inclusive and just world:
- Empathy and Awareness: Cultivate awareness and compassion for the diverse experiences shaped by ascribed status. Acknowledge the privileges and limitations that different individuals face.
- Promote Equal Opportunities: Advocate for policies and initiatives that promote equal access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities for all.
- Challenge Stereotypes: Consciously challenge harmful stereotypes related to race, gender, and other social classifications. Promote diversity and inclusivity in all aspects of life.
- Celebrate Achievements: Recognize and celebrate the achievements of individuals from diverse backgrounds, highlighting their contributions to society.
FAQ
Q: Can someone change their ascribed status?
A: While ascribed status is largely determined at birth, it’s important to note that social change and individual efforts can challenge traditional norms. Individuals can work to change the perceptions and systemic inequalities that arise from ascribed status.
Q: How does education contribute to achieved status?
A: Education provides individuals with knowledge, skills, and credentials, enabling them to access better job opportunities and enhance their social standing.
Q: Is achieved status always a positive thing?
A: Not necessarily. While achievement can be a source of pride and social mobility, it can also lead to competition and social pressure, creating a sense of insecurity or inadequacy.
Q: What role does social mobility play in this context?
A: Social mobility refers to the movement of individuals up or down the social ladder. It can be influenced by both ascribed and achieved status, highlighting the dynamic nature of social stratification.
Ascribed And Achieved Status Examples
Conclusion
Understanding the concepts of ascribed and achieved status is essential for navigating the complex world of social dynamics and inequalities. By recognizing the impact of both assigned and earned positions, we can foster a more just and equitable society that celebrates both individual achievements and collective responsibility.
Are you intrigued by the interplay of ascribed and achieved status? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!





