Imagine a classroom filled with students, each with their own unique talents and aspirations. They’re learning, collaborating, and preparing for their roles in society. But what if this classroom wasn’t just a place for individual growth, but also a microcosm of the broader social system? This is the core concept of functionalism in education, a perspective that views education as an essential mechanism for maintaining and strengthening society.
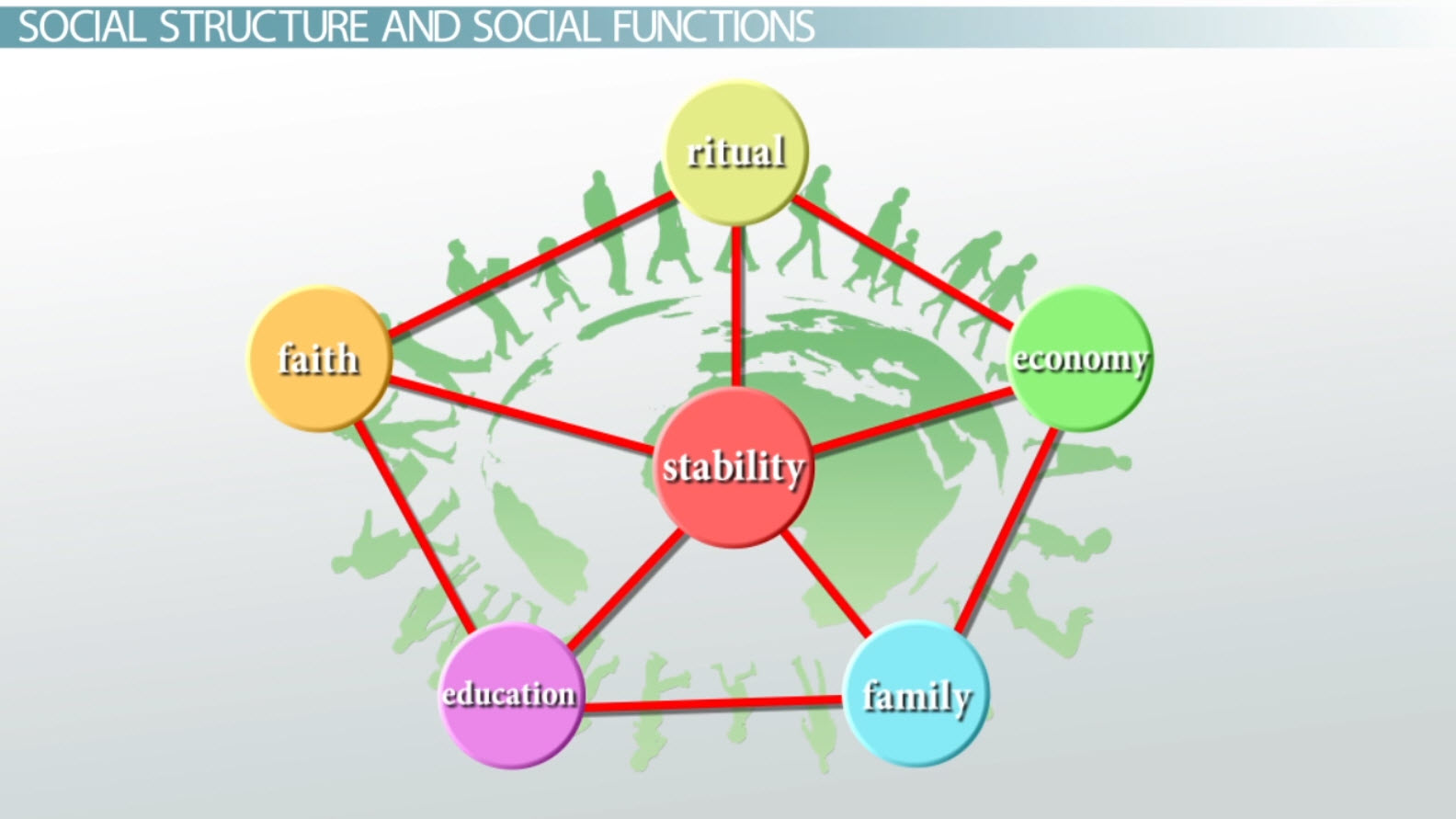
Image: study.com
Functionalism views society as a complex organism, like a human body. Each part, from the heart to the lungs, plays a crucial role in keeping the whole body functioning. Similarly, in a functionalist view, institutions like education, family, and government are interdependent parts that contribute to the overall stability and well-being of society. This viewpoint emphasizes how education contributes to the smooth operation of society by preparing individuals for their roles, promoting social cohesion, and transmitting cultural values.
The Foundations of Functionalism in Education
Early Influences and Key Concepts
The roots of functionalism can be traced back to the works of sociologists like Émile Durkheim and Talcott Parsons, who were influential in shaping the field. Durkheim saw education as a vital force for social solidarity, helping to bind individuals together through shared values, beliefs, and norms. Parsons further developed this concept, arguing that education serves as a conduit for transmitting the dominant cultural values and norms of society, ensuring social stability and harmony.
Manifest and Latent Functions
A central idea in functionalism is the distinction between manifest and latent functions. Manifest functions refer to the intended and explicitly recognized purposes of education, such as teaching literacy, numeracy, and specialized skills. These functions are clearly articulated in school curricula and educational policies. Latent functions, on the other hand, are unintended consequences of education, often less obvious but equally important. These can include socialization, social status attainment, and the development of social networks.
Take, for example, the manifest function of teaching history. Students are expected to learn about the past, key events, and historical figures. However, the latent function of history education is to foster a sense of national identity, common values, and shared heritage. This latent function plays a crucial role in promoting social cohesion and stability.
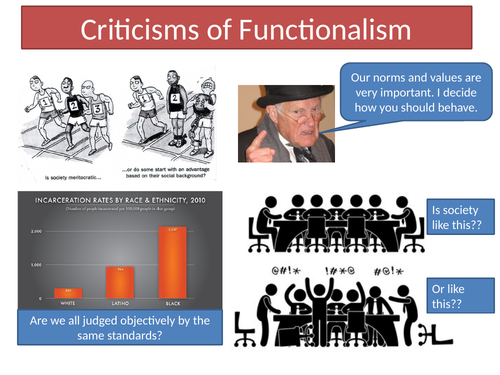
Image: www.tes.com
The Role of Education in Maintaining Society
Socialization and Cultural Transmission
Functionalists see education as a powerful tool for socialization. It’s where children learn the norms, values, beliefs, and behaviors of their society, preparing them for their future roles as responsible citizens. From understanding traffic rules to respecting authority figures, education plays a key role in shaping individual behavior and contributing to social order.
Education also serves as a vehicle for cultural transmission. It passes on knowledge, traditions, and cultural values from one generation to the next, ensuring the continuity and stability of society. This includes teaching history, literature, music, and art, which help preserve and transmit a nation’s cultural heritage.
Skill Development and Economic Productivity
Another crucial function of education is to equip individuals with the skills and knowledge they need to participate effectively in the workforce. The modern economy demands a skilled workforce, and education plays a vital role in meeting this demand by providing individuals with the tools they need to excel in their chosen fields. This is particularly relevant in today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, where continuous learning and adaptation are crucial for success.
The focus on skill development also has social implications. Education can help bridge social inequalities by providing individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds with opportunities to acquire skills that can lead to better jobs and a higher standard of living. This contribution to social mobility is a key element of the functionalist perspective on education.
Social Selection and Social Stratification
Functionalists acknowledge that education plays a role in social stratification, the hierarchal arrangement of individuals and groups in society. They argue that education serves as a mechanism for social selection, sorting individuals into different social roles and positions based on their abilities and achievements.
This social selection process is often seen as a meritocratic system, where individuals are rewarded based on their efforts and talents. However, critics argue that the meritocratic ideal is not always achieved, as factors such as socioeconomic background and access to resources can have a significant impact on educational outcomes. This raises important questions about the fairness and equality of the education system, leading to debates about the role of social mobility and opportunity in a functionalist framework.
Criticisms of the Functionalist Perspective
Focus on Consensus and Stability
While functionalism highlights the role of education in maintaining societal stability, critics argue that it overlooks the potential for conflict and social change. Critics argue that the focus on consensus and stability can lead to a neglect of power dynamics and inequalities that exist within societies, potentially overlooking the voices of marginalized groups or those who challenge the status quo.
Overemphasis on Social Control
Some critique the functionalist perspective for portraying education as a tool for social control. They argue that the emphasis on transmitting dominant values and norms may stifle individual expression and limit critical thinking. This can lead to a reproduction of existing power structures and societal inequalities, perpetuating the status quo rather than promoting social progress.
Functionalism in Education: A Contemporary Perspective
Adapting to a Changing World
In the 21st century, the challenges and demands on education have evolved significantly. The rise of technology, globalization, and increasing social complexity have created new challenges for educators. However, the functionalist perspective can still offer valuable insights into how education can adapt to these changes. It highlights the need for education to equip students with the skills and knowledge they need to navigate a rapidly changing world, including critical thinking, adaptability, and communication skills.
Addressing Inequality and Promoting Inclusion
The functionalist perspective also emphasizes the importance of addressing social inequalities in education. This includes efforts to close achievement gaps, create equitable access to resources, and foster inclusive environments. By promoting inclusivity and addressing inequalities, education can become a more powerful force for social progress and social mobility.
Beyond Traditional Functions
While the traditional view of functionalism emphasizes the role of education in maintaining social order and stability, contemporary perspectives recognize the potential for education to go beyond these functions. Education can also play a role in promoting innovation, creativity, and social change. It can foster critical thinking, empower individuals to question the status quo, and contribute to the development of a more just and equitable society.
Functionalism On Education
Conclusion: The Evolution of Functionalism in Education
Functionalism in education remains a valuable framework for understanding how the educational system interacts with broader social structures and processes. It provides a starting point for exploring how education contributes to the overall functioning of society, the transmission of cultural values, and the development of skills needed for economic participation. While criticisms of the functionalist perspective exist, particularly regarding its emphasis on social control and its potential limitations in addressing social inequalities, it continues to inform discussions about the purpose and evolution of education. In an era of rapid change and increasing social complexity, functionalism offers a lens for understanding the challenges and opportunities facing education systems around the world.
This essay has provided a brief overview of functionalism in education. To delve deeper into this topic, consider exploring resources from sociologists such as Émile Durkheim, Talcott Parsons, and Robert Merton. You can also explore contemporary scholarship that examines the role of education in addressing social inequalities and promoting social progress. Share your thoughts on how functionalism applies to education in your own experiences and perspectives. The conversation about the purpose and role of education is ongoing, and your insights are valuable.





