Have you ever considered the unintended consequences of a seemingly simple act? Think about the popularity of a certain fashion trend, the rise of a new technology, or even the enactment of a new law. These things often have unforeseen outcomes that can ripple through society in ways we might not immediately realize. This is where the concept of latent functions in sociology comes in. It’s a fascinating lens through which we can analyze the complex and often hidden meanings behind human behavior and social institutions.

Image: www.vrogue.co
Latent functions, in a nutshell, are the unintended and often unrecognized consequences of social actions. They stand in contrast to manifest functions—the intended and obvious outcomes of social actions. While we might understand the intended purpose of a school, for example, its latent functions could include fostering social relationships, developing a sense of community amongst its students, or even providing a safe haven for children during challenging times. Understanding latent functions provides deeper insights into the dynamics of society and helps us see beyond the surface of social phenomena.
The Birth of a Concept: Tracing Latent Functions’ Origins
From Functionalism to Unveiling Hidden Meanings
The concept of latent functions originated with the functionalist school of sociology, which emerged in the early 20th century. Functionalists viewed society as a complex system of interconnected parts, each serving a specific function to maintain the stability and order of the whole. Foundational thinkers like Émile Durkheim and Talcott Parsons emphasized the importance of social institutions in shaping individual behavior and maintaining social cohesion. While focusing on the intended functions of these institutions, they also recognized that social actions could have unanticipated consequences that contributed to the overall functioning of society.
Robert Merton: A Turning Point in Understanding Latent Functions
Sociologist Robert K. Merton played a pivotal role in further developing the concept of latent functions, refining it and applying it to a broader range of social phenomena. In his 1949 work, *Social Theory and Social Structure*, Merton highlighted the distinction between manifest and latent functions, arguing that the latter could be just as important as the former in shaping society. He also emphasized that latent functions could be positive, negative, or neutral, and that they often came into play in unexpected ways.
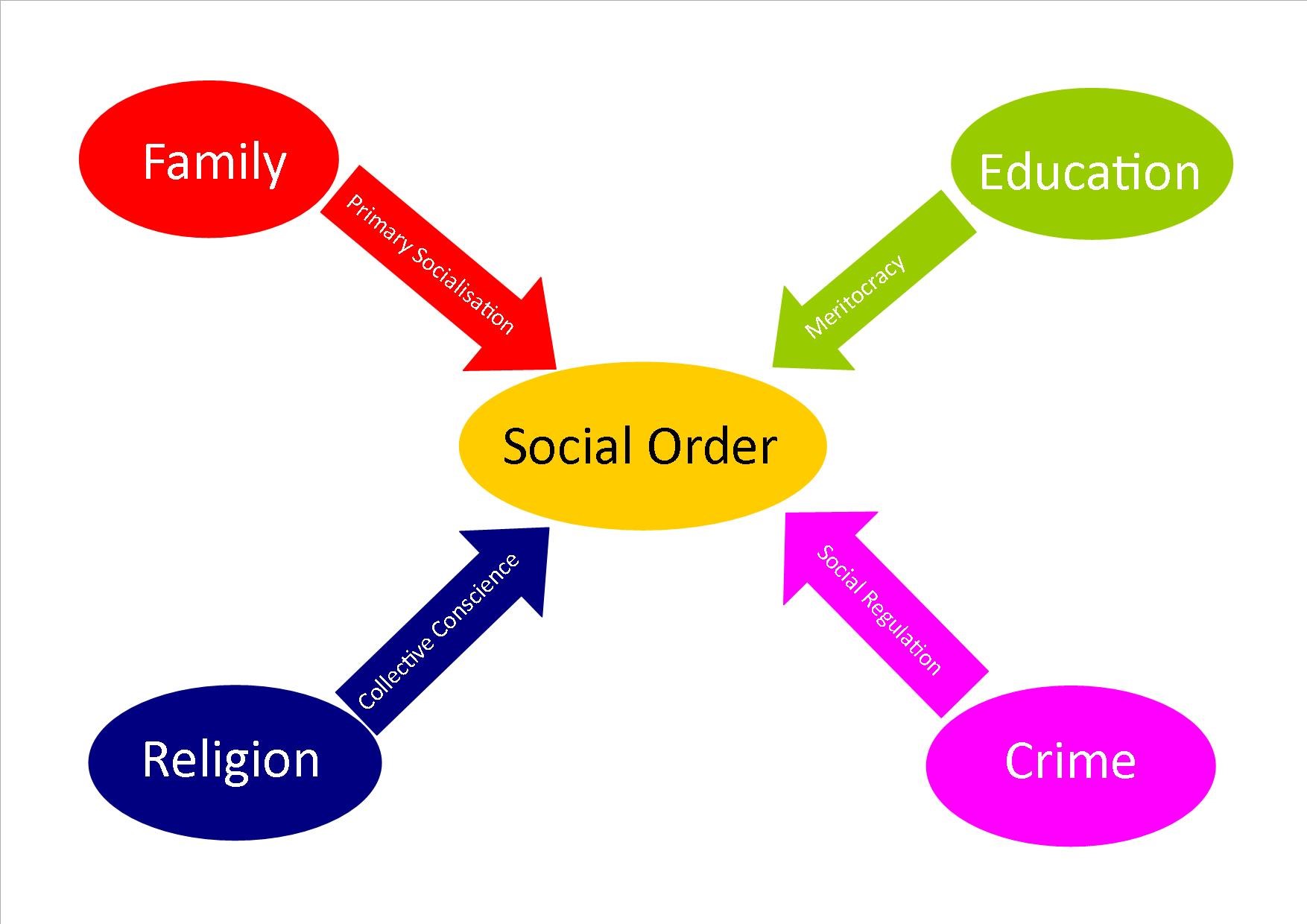
Image: www.tutorsploit.com
Examples of Latent Functions in Action
Latent functions can be found across various aspects of social life, from the seemingly mundane to the most complex social institutions. Here are a few illustrative examples:
The Latent Functions of Education
While the manifest function of education is to impart knowledge and skills, it also serves several latent functions:
- Socialization: Schools teach students societal norms, values, and expectations, shaping their behavior and preparing them for adult life.
- Social Networking: Schools provide opportunities for students to form friendships, build social networks, and develop interpersonal skills.
- Identity Formation: Schools contribute to the development of a sense of identity, as students interact with peers, navigate social structures, and build self-confidence.
- Delaying Entry into the Workforce: Education can function as a buffer for young people, providing a period of time for them to mature and prepare for the demands of the workforce.
The Latent Functions of Social Media
The rapid growth of social media platforms has led to a shift in how we communicate and interact with the world around us. While the manifest function of these platforms is to connect people, they also have unforeseen consequences:
- Echo Chambers and Polarization: Social media algorithms can create filter bubbles, exposing users primarily to information that aligns with their existing views, further reinforcing their opinions and potentially leading to a more polarized society.
- Mental Health Impacts: Constant exposure to curated and often idealized versions of reality on social media can contribute to feelings of inadequacy, anxiety, and depression.
- Spread of Misinformation: The viral nature of social media can facilitate the rapid spread of false or misleading information, making it difficult to discern truth from fiction.
The Latent Functions of Fashion
Fashion, often seen as a purely aesthetic pursuit, can carry a deeper social significance. Its latent functions can reflect societal values, power dynamics, and cultural trends:
- Social Status and Identity: Clothing choices can signal social status, group affiliation, and personal identity, influencing how others perceive us and how we see ourselves.
- Gender Roles and Expectations: Fashion choices can reinforce or challenge traditional gender norms and expectations, reflecting societal attitudes toward gender roles.
- Cultural Transmission: Fashion trends can spread across different cultures and societal groups, influencing the way people dress and shaping cultural identities.
The Latent Functions of Religion
Religion, with its deeply ingrained beliefs and practices, is often considered a cornerstone of many cultures. Beyond fulfilling its manifest function of providing spiritual guidance and moral frameworks, religion can also:
- Social Support Networks: Religious communities offer social support, a sense of belonging, and shared values, fostering social cohesion and reducing feelings of isolation.
- Social Control: Religious teachings can influence moral norms and values, shaping individual behavior and providing a framework for social order.
- Political Mobilization: Religious groups can play a significant role in political movements and campaigns, advocating for social change and influencing public policy.
The Importance of Studying Latent Functions
Understanding latent functions is crucial for various reasons:
Gaining a Deeper Understanding of Society
By examining the unintended consequences of social actions, we gain a more nuanced understanding of how society functions. Latent functions highlight the complexity and interconnectedness of social systems, revealing how seemingly unrelated events can influence one another.
Identifying Social Problems and Solutions
Latent functions can help us identify unforeseen social problems stemming from social policies and actions. By understanding these unintended consequences, we can develop more effective solutions to address social issues and minimize negative outcomes.
Promoting Social Change
Recognizing the latent functions of social institutions and practices can empower us to challenge existing structures and advocate for positive change. By understanding the hidden meanings behind social phenomena, we can work toward creating a more equitable and just society.
Current Trends and Future Directions
The study of latent functions continues to evolve and adapt as society itself changes. Emerging technologies, globalization, and social movements are reshaping the landscape of social interaction, bringing new dimensions to the concept of latent functions.
The Impact of Social Media
The rise of social media has heightened the significance of understanding latent functions. Social media’s rapid spread and influence have unleashed a multitude of unanticipated consequences, requiring new research and analytical approaches to navigate these complex social dynamics.
Interdisciplinary Approaches
The study of latent functions is becoming increasingly interdisciplinary, encompassing fields such as psychology, anthropology, and communication studies. These diverse perspectives provide a richer understanding of the multifaceted nature of social phenomena.
The Need for Ethical Considerations
As our understanding of latent functions grows, it’s crucial to consider the ethical implications of our research and applications. It’s important to ensure that our analyses are responsible, avoid perpetuating harmful stereotypes, and promote social good.
Latent Functions Sociology
https://youtube.com/watch?v=LcluY6UsVXY
Conclusion
The concept of latent functions offers a valuable lens through which we can analyze the intricate workings of society. By considering the unintended consequences of social actions, we gain a deeper understanding of the dynamic, interconnected nature of social systems. Exploring latent functions not only sheds light on the complexities of social life but also empowers us to identify social problems, work towards positive change, and create a more informed and engaged society.
If you’re interested in learning more about latent functions, I encourage you to delve into additional resources, such as academic journals, books, and online articles. You can also explore the works of influential sociologists like Robert K. Merton, Émile Durkheim, and Talcott Parsons. By engaging with this fascinating concept, we can continue to unlock the hidden meanings behind our social world and contribute to a better understanding of ourselves and our place in society.





