Imagine a world where every culture was an isolated island, untouched by the influences of others. A world without the spicy warmth of Indian curries in London, the vibrant sounds of K-Pop echoing through American streets, or the intricate patterns of Moroccan tiles adorning Italian homes. This scenario, while intriguing in its isolation, would deprive us of the richness and diversity that comes from the interconnectedness of cultures. It’s the very nature of cultural diffusion, the dynamic exchange of ideas, customs, beliefs, and technologies across geographical and social boundaries, that weaves the vibrant tapestry of global cultures we see today.
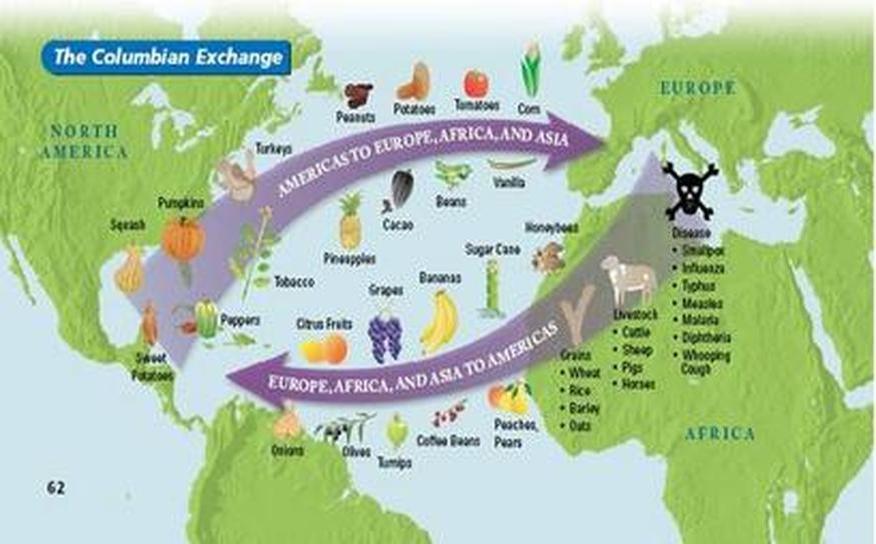
Image: ar.inspiredpencil.com
Understanding cultural diffusion isn’t simply about knowing how things spread. It’s about deciphering the complex interplay of forces that shape our world – the factors that propel innovation, the bridges that connect continents, and the influences that redefine our identities. This exploration sheds light on the mechanisms behind everything from the global popularity of smartphones to the impact of ancient Roman law on modern legal systems.
Unpacking the Fundamentals: Defining and Classifying Cultural Diffusion
At its core, cultural diffusion is the process of cultural traits being transmitted from one group to another. These traits can range from material objects like clothing and tools to intangible elements like language, religion, and artistic expressions. Think of it as a ripple effect: A small change in one culture can create waves of influence that reach far and wide.
To better understand this process, it’s helpful to categorize the different ways cultural diffusion occurs. The dominant classifications are:
- Direct Contact: This is the most straightforward form, where cultures directly interact with one another, leading to the exchange of ideas and practices. Think of trade routes that connected ancient civilizations, sharing knowledge and goods, or the multicultural melting pot of modern cities where different communities intermingle.
- Relocation Diffusion: This involves the movement of people from one location to another, bringing their culture with them. The spread of Christianity across Europe, driven by missionary travels, or the influence of Indian cuisine in the United Kingdom, brought by Indian immigrants, are prime examples.
- Hierarchical Diffusion: This occurs when ideas and trends spread from centers of power or influence, often through social elites or institutions. The adoption of latest fashion trends from high-end designers cascading down to mainstream consumers is an example, and even something as seemingly innocuous as the spread of the “selfie” phenomenon, initiated by celebrities, exemplifies this pattern.
- Contagious Diffusion: This is similar to contagious diseases, where traits spread rapidly and widely from person to person through proximity and interaction. Think about the viral spread of internet memes, the popularity of certain musical genres like rock and roll, or the rapid adoption of new technologies like smartphones, all driven by peer influence and social networks.
- Stimulus Diffusion: Unlike direct adoption, this involves stimulating an idea in a new culture, leading to its independent evolution. The invention of the printing press in Europe, for instance, inspired the development of printing technologies in other parts of the world, leading to unique adaptations based on local needs and resources.
Exploring the Dynamics of Cultural Diffusion
Understanding the types of cultural diffusion is just the first step. To truly grasp its impact, we need to delve into the driving forces behind it. These factors can be categorized as:
- Economic Factors: Trade, globalization, and access to resources play a crucial role in cultural exchange. The silk road, for example, facilitated the spread of Eastern philosophies, fashion, and artistic traditions towards the West, while global trade today brings us a plethora of culinary delights from diverse corners of the world.
- Political Factors: Colonialism, migration policies, and political alliances all influence the movement of people and ideas. The French colonization of parts of Africa, for example, left a lasting impact on linguistic, cultural, and political structures. Similarly, the global interconnectedness fostered by international organizations like the United Nations facilitates the spread of ideas and collaborations across borders.
- Technological Factors: Rapid advancements in communication and transportation technologies have accelerated the pace of cultural diffusion. The internet and social media have created unprecedented platforms for cultural exchange, allowing information and trends to spread at lightning speed. Travel and tourism have also brought cultures closer, promoting understanding and shared experiences.
- Social Factors: Demographic shifts, cultural values, and social interactions are deeply intertwined with cultural diffusion. The increasing urbanization of societies brings diverse people together, leading to cultural fusion and innovation. Social movements, such as the global fight for gender equality, can also generate cultural shifts and the adoption of new values and practices.
The Ripple Effect: Consequences of Cultural Diffusion
Cultural diffusion, while undeniably fascinating, also carries a complex set of consequences. Positive outcomes include:
- Increased Innovation and Creativity: The fusion of cultures can spark new inventions, artistic styles, and ideas. The blending of European and Asian culinary traditions, for example, gave birth to fusion cuisine, redefining culinary experiences.
- Enhanced Global Understanding and Tolerance: Exposure to diverse cultures can foster empathy, dismantle stereotypes, and promote respect for different values and perspectives.
- Economic Boost: Cultural exchange can stimulate trade, tourism, and global economic connections, contributing to economic development and prosperity.
However, cultural diffusion also gives rise to potential challenges:
- Cultural Homogenization: The dominance of certain cultures over others can lead to the erosion of local traditions and the homogenization of global culture. The spread of fast food chains and the dominance of Western popular culture are examples of this phenomenon.
- Cultural Appropriation: The misappropriation of cultural expressions without understanding or respect for their origin can be harmful and disrespectful.
- Conflict and Tension: The clash of cultural values and beliefs can sometimes lead to misunderstandings, social unrest, and even conflict.

Image: study.com
Types Of Cultural Diffusion
A Look Towards The Future: Navigating the Dynamics of Cultural Diffusion
In a world increasingly interconnected by technology, globalization, and migration, understanding the mechanisms of cultural diffusion is more crucial than ever. As cultures continue to interact and influence one another, our ability to navigate the potential benefits and challenges of these exchanges will be key to fostering a world where diversity thrives, innovation flourishes, and mutual respect prevails.
As we embrace the richness of this global cultural tapestry, it’s essential to approach cultural diffusion with mindful awareness. We must champion the positive aspects of cultural exchange, while being vigilant against the potential pitfalls of homogenization and appropriation. Ultimately, by understanding the nuanced dynamics of cultural diffusion, we can create a more culturally inclusive and harmonious world for generations to come.





