Have you ever stopped to ponder the unintended consequences of a seemingly simple act, like attending a sporting event or joining a social club? These actions often have clear, intended outcomes, but they can also trigger a myriad of unexpected and often beneficial effects that go unnoticed. This fascinating phenomenon is at the heart of functionalist sociology, which examines social structures and institutions through the lens of their manifest and latent functions.
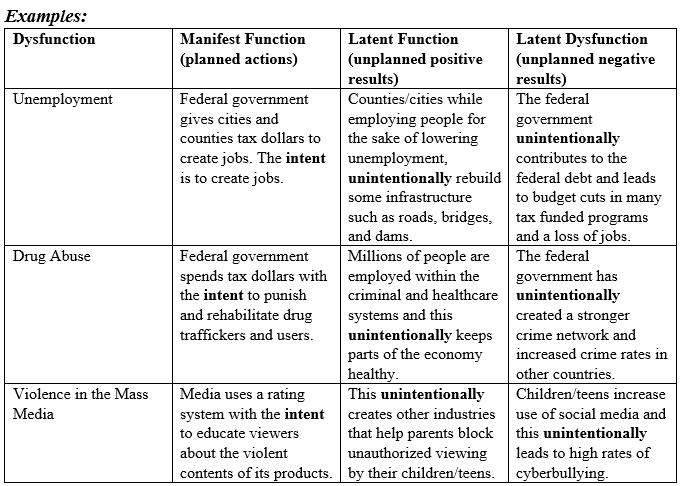
Image: www.mypromosource.com.au
Understanding the concepts of manifest and latent functions is crucial for comprehending the complex dynamics of society. It allows us to appreciate how seemingly mundane activities or institutions can have profound, unanticipated impacts, shaping our social fabric in ways we might not even realize. In this article, we will delve into the world of manifest and latent functions, exploring their definitions, historical context, and real-world examples that illustrate their intricate interplay in our daily lives.
The Foundations of Functionalism: A Brief History
From Durkheim to Merton: Tracing the Conceptual Evolution
The concept of manifest and latent functions can be traced back to the pioneering work of Émile Durkheim, a founding father of modern sociology. Durkheim, in his seminal work *The Division of Labor in Society* (1893), emphasized the importance of social solidarity and the role of institutions in maintaining social order. He saw society as a complex system, with each part contributing to its overall functioning.
Robert K. Merton, a prominent sociologist of the 20th century, built upon Durkheim’s framework, introducing the distinction between manifest and latent functions. In his 1949 publication *Social Theory and Social Structure*, Merton argued that social phenomena, including institutions and social practices, can have both intended and unintended consequences. He coined the terms *manifest functions* to refer to the recognized and intended consequences of social actions, while *latent functions* denoted the unrecognized and unintended consequences.
Deciphering the Concepts: Manifest and Latent Functions Defined

Image: www.vrogue.co
Manifest Functions: The Intended Outcomes
Manifest functions are the observable and intended consequences of social actions or institutions. They represent the explicit goals, objectives, and purposes for which a social phenomenon exists. For example, the manifest function of education is to impart knowledge and skills to individuals, preparing them for future roles in society. This is the primary goal of educational institutions and the intended outcome of the educational process.
Latent Functions: The Unforeseen Consequences
Latent functions, on the other hand, are the unintended and often unrecognized consequences of social actions or institutions. They represent the hidden or unanticipated effects that emerge alongside the manifest functions. For example, a latent function of education might be the creation of social networks among students, which can lead to career opportunities and lifelong friendships. This outcome is not the primary goal of education but arises as a byproduct of the educational experience.
Illuminating Examples: Unveiling the Hidden Layers
The Case of Sports: More Than Just a Game
Consider the seemingly simple act of attending a sporting event. The manifest function is clear: entertainment and enjoyment. People attend sports events to experience the thrill of competition, cheer for their favorite teams, and escape from everyday life. However, sports have a plethora of latent functions, which contribute significantly to the social fabric.
Sports foster a sense of community and shared identity, uniting people from diverse backgrounds under a common banner. They provide opportunities for socialization, physical activity, and even career development. Furthermore, professional sports can stimulate local economies, generate tourism, and promote social cohesion through shared passions and celebrations.
The Unexpected Benefits of Social Media: Connecting and Contesting
Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have become ubiquitous in modern society. The manifest function of these platforms is to facilitate communication, connect people, and share information. However, social media also harbor an array of latent functions.
Social media platforms have become a powerful tool for social activism, allowing individuals to organize protests, raise awareness about social issues, and challenge existing power structures. They have also become a platform for political discourse, enabling individuals to engage in debates, express their opinions, and participate in the democratic process. Yet, these platforms also come with their own set of unintended consequences, such as the spread of misinformation, cyberbullying, and polarization of opinions.
Education: More Than Just Academics
Schools, as institutions, have the primary manifest function of imparting knowledge and skills. They aim to prepare students for the workforce, develop critical thinking abilities, and foster intellectual growth. However, education also serves several latent functions, shaping the social landscape in unexpected ways.
Schools act as socializers, transmitting cultural values and norms, shaping individuals’ perceptions of themselves and society. They provide opportunities for socialization, fostering friendships and peer interactions. Education also contributes to social mobility, enabling individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds to improve their socioeconomic standing through access to knowledge and skills.
The Power of Perspective: Recognizing the Subtleties
Examining social phenomena through the lens of manifest and latent functions encourages us to move beyond superficial interpretations and explore the deeper, often hidden, consequences of social actions. By recognizing both the intended and unintended outcomes, we gain a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding of how society operates and evolves.
Furthermore, understanding the interplay of manifest and latent functions helps us identify potential problems and develop solutions. For example, by recognizing the latent function of social media in spreading misinformation, we can devise strategies to combat fake news and promote media literacy. Similarly, by recognizing the latent function of education in social mobility, we can develop policies to improve access to quality education for underserved communities.
Manifest And Latent Functions Examples
https://youtube.com/watch?v=LcluY6UsVXY
A Path Forward: Embracing Complexity and Seeking a Deeper Understanding
The study of manifest and latent functions is a powerful tool for analyzing the intricate dynamics of society. It reminds us that social phenomena are rarely simple, with actions and institutions often producing a tapestry of both intended and unintended consequences. By adopting a critical and holistic approach to social analysis, we can gain a more profound understanding of the forces that shape our world, enabling us to address societal challenges and foster a more equitable and just society.
To learn more about manifest and latent functions, explore the rich body of sociological literature, including the works of Émile Durkheim, Robert K. Merton, and other prominent sociologists. Engage in critical discussions about the impact of various social phenomena, paying attention to both the manifest and latent functions. By expanding our understanding of these powerful concepts, we can develop a more nuanced and insightful view of the complex world we inhabit.





