Imagine a classroom filled with eager students, their eyes glued to the whiteboard as a teacher explains a complex scientific concept. The immediate goal is clear: to impart knowledge and foster understanding. But what if this seemingly ordinary setting holds hidden, unintended consequences that shape the lives of these students beyond the curriculum? This is the realm of latent functions in education, a concept that delves into the unexpected and often overlooked effects of our formal learning environments.
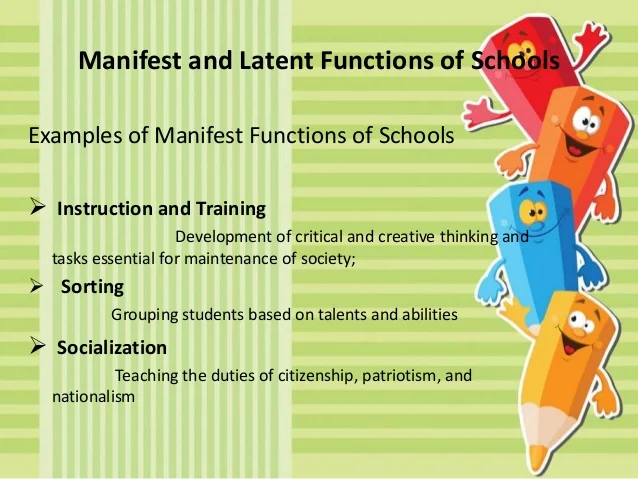
Image: keplarllp.com
While we readily acknowledge the obvious functions of education, such as transmitting knowledge and developing skills, the concept of latent functions suggests a deeper, more nuanced impact. It is in these hidden effects that we discover the true power of education, shaping not only academic outcomes but also social, cultural, and personal development. This article will explore the vast and fascinating landscape of latent functions in education, uncovering the hidden forces that shape our lives in ways we often fail to recognize.
Beyond the Textbooks: Unveiling the Latent Functions
The term “latent function” was coined by the sociologist Robert K. Merton, who argued that social institutions, including education, have both manifest (intended) and latent (unintended) consequences. While the manifest function of education is clear – to impart knowledge and skills – latent functions can be subtle and often surprising.
1. Socialization and Values
One of the most significant latent functions of education is socialization. School serves as a microcosm of society, providing a space for students to learn and internalize social norms, values, and expectations. Children interact with diverse peers, develop a sense of community, and learn the unwritten rules of social interaction. Schools are not just places of learning, but also crucibles of social development, shaping the individuals who will eventually become contributing members of society.
2. Cultural Transmission and Identity
Education plays a vital role in preserving and transmitting cultural heritage. Through history lessons, literature studies, and artistic expression, students are exposed to the rich tapestry of their own culture and the cultures of others. This process fosters a sense of shared identity and helps individuals navigate the complexities of a multicultural world. Schools become spaces where cultural values are perpetuated and celebrated, contributing to a shared understanding of history, traditions, and beliefs.

Image: www.youtube.com
3. Building Social Networks
School provides opportunities for students to build valuable social networks that can have lasting impacts on their lives. From friendships formed in classrooms and extracurricular activities to connections made with teachers and mentors, the relationships cultivated in school become a vital source of support, guidance, and opportunities throughout life.
4. Delayed Entry into the Labor Market
While this may seem like a negative consequence, it’s crucial to consider the long-term benefits of delayed entry into the workforce. Education allows young adults to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary for a successful career while simultaneously fostering personal growth and development. This “time out” from the working world provides an opportunity for individuals to explore their interests, develop critical thinking skills, and gain a broader perspective on life.
5. Social Control and Conformity
Schools are often seen as agents of social control, subtly shaping the behavior and beliefs of students. Through enforced rules, standardized tests, and the promotion of certain values, education systems can contribute to a more homogeneous social order. This, however, comes with its own set of challenges, as it can sometimes stifle individuality and creativity.
The Dark Side: Latent Dysfunctions in Education
While the latent functions of education can be profoundly positive, it is crucial to acknowledge the potential downsides. Just as positive outcomes can emerge from unintended consequences, negative consequences, or dysfunctions, can also arise.
1. Social Stratification and Inequality
The unequal distribution of resources and opportunities within education systems can exacerbate existing social inequalities. Schools in affluent neighborhoods often receive greater funding and have access to better resources, leading to a disparity in educational outcomes for students from different socioeconomic backgrounds. The cycle of privilege can perpetuate itself, creating a vicious cycle where students from underprivileged communities are disproportionately disadvantaged.
2. The “Hidden Curriculum”
The concept of the “hidden curriculum” refers to the informal, often unacknowledged messages and values that students absorb in school. This can include biases in textbooks, classroom interactions, and the social dynamics within schools. The hidden curriculum can perpetuate stereotypes, reinforce traditional gender roles, and limit opportunities for marginalized students. Recognizing and addressing the hidden curriculum is crucial to creating a more equitable and inclusive educational environment.
3. The “Credentialed Society”
Education is often seen as a path to social mobility, but in some cases, it can lead to a focus on qualifications for the sake of qualifications. This can create a “credentialed society” where individuals become obsessed with obtaining certificates and degrees, regardless of whether they actually possess the knowledge or skills to succeed in their chosen fields. This emphasis on credentials can be detrimental to true learning and innovation.
4. The “Over-Testing” Phenomenon
The increasing reliance on standardized testing has become a major concern in contemporary education. While assessments are important for evaluating progress, over-emphasizing standardized tests can lead to a narrow curriculum, a focus on rote memorization over critical thinking, and undue stress for students. This can ultimately hinder true learning and undermine the pursuit of education for its own sake.
Navigating the Complexities: The Ongoing Debate
The debate surrounding latent functions in education is ongoing and nuanced. While many acknowledge the positive contributions of education to social development and personal growth, there is also a critical awareness of the potential pitfalls. It is essential to approach this topic with a balanced perspective, recognizing both the potential benefits and drawbacks of these hidden influences.
1. The Power of Education Reform
Addressing the potential dysfunctions of education requires a commitment to reform. This involves reimagining curriculum design, promoting inclusive learning environments, addressing social inequalities, and acknowledging the diverse needs and experiences of students. By investing in teachers, supporting research, and prioritizing equity, education systems can mitigate the negative consequences of latent dysfunctions and ensure that education serves as a force for positive change.
2. Fostering Critical Thinking and Self-Awareness
Beyond institutional reforms, it is crucial to foster critical thinking and self-awareness among students. Encouraging students to question assumptions, challenge biases, and develop their own perspectives is essential for navigating the complex landscape of latent functions. Education should not only equip individuals with knowledge and skills but also empower them to be critical consumers of information and active participants in society.
Latent Function In Education
Conclusion
The latent functions of education are a powerful testament to the multifaceted nature of learning. While the intended goals of education are undeniable, the hidden consequences that unfold in classrooms and beyond shape our lives in profound ways. By understanding these latent functions, we can appreciate the full potential of education, both its strengths and its limitations, and strive to create a more equitable, meaningful, and empowering educational experience for all.
This article has only scratched the surface of the vast and complex world of latent functions in education. There is much more to explore and understand. We encourage you to continue your journey of discovery by engaging in thought-provoking discussions, reading relevant research, and reflecting on your own experiences with education. Together, let us strive to harness the power of education to create a brighter future for ourselves and generations to come.





