Picture a bustling city, a symphony of activity where countless individuals interact, each playing a vital role in the grand scheme. From the barista crafting your morning coffee to the bus driver navigating the traffic, to the doctor tending to the sick, each person contributes to the larger social fabric. This complex tapestry of human interaction is what sociologists dedicate their lives to understanding, and one of the most influential theories in this field is Functionalism.
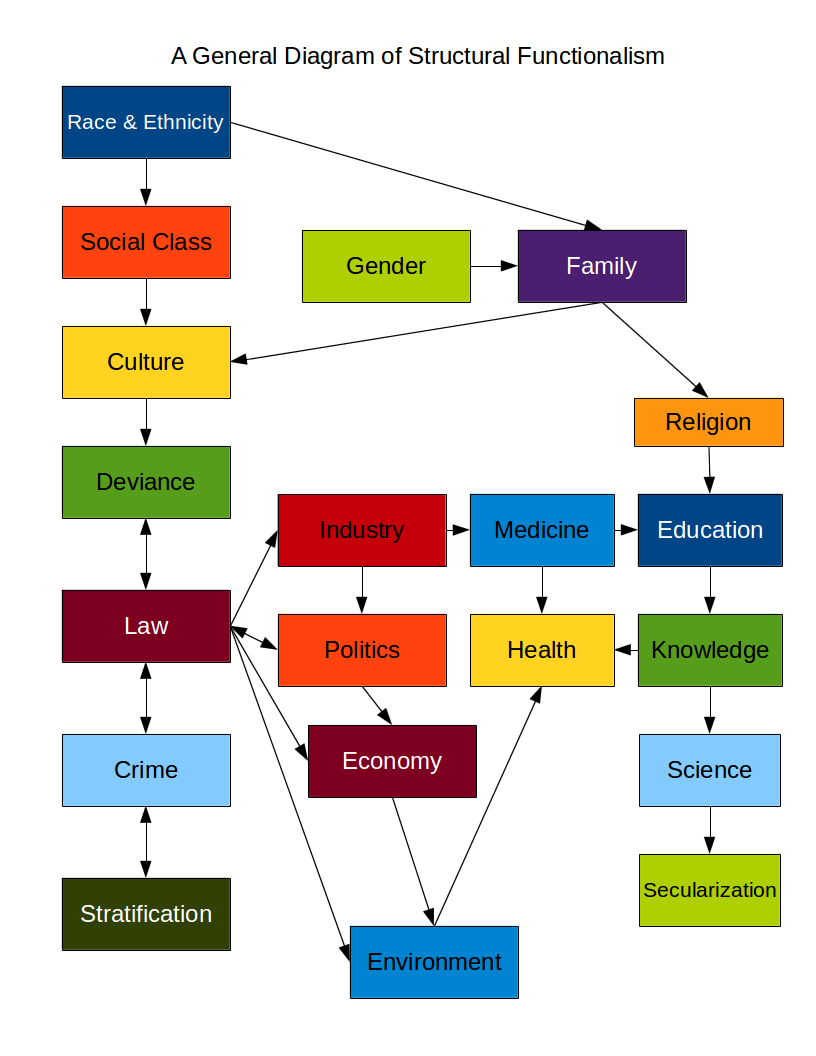
Image: www.writework.com
But what exactly is Functionalism, and why should we care about it? This sociological perspective, developed in the early 20th century, views society as a living organism, with each part, like a vital organ, contributing to its overall health and functionality. It’s through this lens that we can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of our communities, unraveling the intricate workings of our social structures and the consequences of disruptions within them.
A Society in Harmony: The Foundational Principles of Functionalism
The core idea behind Functionalism is straightforward: society operates as a cohesive system where various components, from institutions like education and government to social roles like parents and teachers, all work together to maintain order and stability. Imagine each element as a cog in a well-oiled machine, each playing its part to ensure smooth operation.
One of the pioneers of Functionalism, Émile Durkheim, argued that societal solidarity, the glue that binds us together, is achieved through two primary mechanisms: mechanical solidarity and organic solidarity. In simpler societies, mechanical solidarity based on shared beliefs and traditions reigns supreme. Think of a small rural community where everyone is involved in agriculture, their lives intertwined by common values and customs. On the other hand, organic solidarity, prevalent in modern, complex societies, arises from the interdependence of specialized roles. Each individual contributes to the whole, their actions forming a complex web of interconnected activities.
Functionalism in Action: Real-World Examples
Functionalism’s influence extends far beyond the realms of academics. From understanding the impact of social institutions to analyzing social change, its principles offer valuable frameworks for navigating the complexities of our world. Let’s delve into some real-world examples:
The Importance of Education
The educational system, according to functionalist theory, serves a critical function in society: to equip individuals with the knowledge, skills, and values necessary to contribute meaningfully. It serves as a vital mechanism for social mobility, allowing people to climb the social ladder through achievement and merit. By transmitting cultural values and fostering social cohesion, education ensures that individuals are prepared to take on their roles within society.
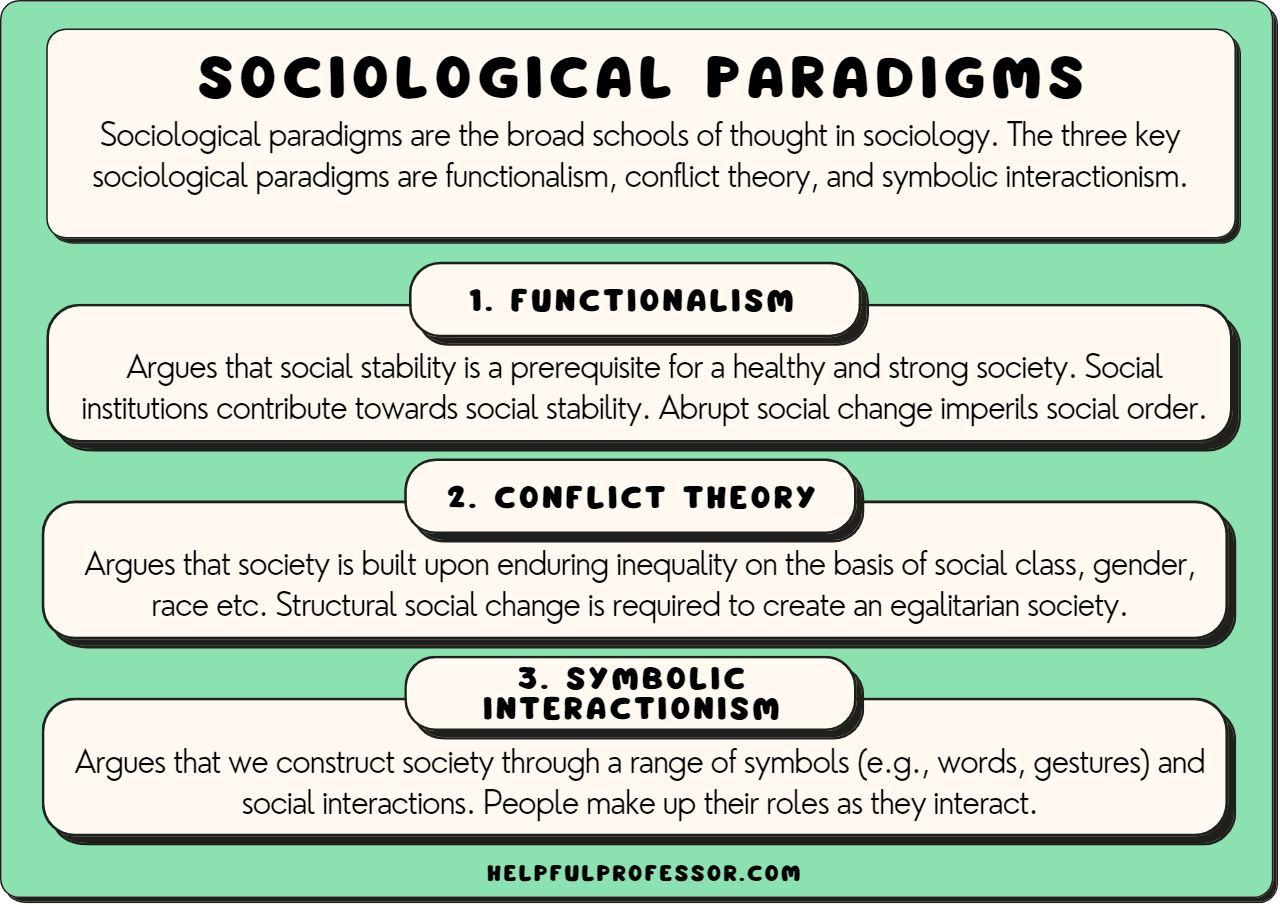
Image: issemonsters.weebly.com
The Role of the Family
Family is often considered the cornerstone of society. From a functionalist perspective, families play a crucial role in socializing children, teaching them fundamental social norms and values, as well as providing emotional support and a sense of belonging. This institution helps to ensure the stability and continuity of society by passing on cultural traditions and nurturing responsible individuals.
The Significance of Religion
Religion, in many societies, acts as a powerful force in maintaining social order. It offers a moral code, a sense of purpose and meaning, and a shared set of beliefs that bind individuals together. Functionalism views religion as a powerful tool for social control, promoting conformity and reinforcing societal norms.
The Dynamics of Social Change
While Functionalism emphasizes stability and order, it also acknowledges the inevitability of social change. This change, according to the theory, arises when there is a disruption in the equilibrium of the social system. For example, the introduction of new technologies, economic shifts, or political upheavals can all act as catalysts for social change.
Critiquing Functionalism: Perspectives Beyond Order and Harmony
While Functionalism offers a valuable framework for examining society, it’s not without its limitations. Critics point out that it overemphasizes social harmony and stability, neglecting power dynamics and conflict that inevitably exist within any society. Some argue that Functionalism perpetuates a conservative view by justifying existing social structures, even if they are detrimental to certain groups or individuals.
Beyond Order: Incorporating Conflict and Power Dynamics
Conflict Theory, a contrasting approach to Functionalism, emphasizes the inherent clash of interests among different groups in society. It argues that social structures are not necessarily designed for harmonious coexistence but rather reflect the power dynamics and inequalities prevalent in societies. This perspective highlights issues of social stratification, inequality, and the struggle for resources and power.
Diverse Perspectives: The Need for a Multifaceted Approach
Understanding society requires a multifaceted approach, integrating various theoretical perspectives. While Functionalism shines a light on the interconnectedness and balance within social systems, it’s essential to consider other perspectives, such as Conflict Theory and Symbolic Interactionism, to obtain a more complete and nuanced understanding of the complexities of social life.
Embracing Functionalism: Insights for a More Cohesive Society
Despite its limitations, Functionalism offers valuable insights into the workings of societies and provides a framework for understanding social change. By examining the interconnectedness of social systems and the roles played by different institutions and individuals, we can develop a greater appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that govern our lives.
It’s important to recognize that society is not static – it is constantly evolving and adapting to new challenges. Understanding Functionalism’s key principles can help us navigate these changes effectively, fostering a more cohesive and harmonious society.
Sociology Functionalist Theory
Exploring Further: Resources and Insights
For those seeking a deeper dive into the world of Functionalism, there are numerous resources available. Start by delving into the works of Émile Durkheim, Talcott Parsons, and Robert Merton, influential figures who shaped the development of this sociological theory.
Share your thoughts on this article and your own perspectives on Functionalism. Have you noticed its principles at play in your daily life? Let’s engage in a meaningful dialogue about the social systems that shape our world!





