Imagine a moment when a simple cough or sneeze sends a jolt of pain shooting down your leg. This is the reality for countless individuals living with a broad disc protrusion. The complex anatomy of your spine, with its intricate network of nerves and cushioning discs, can be susceptible to issues like disc protrusions. While the term may seem intimidating, understanding what it means and exploring treatment options can empower you to manage this condition effectively.

Image: www.medicalexhibits.com
A broad disc protrusion is not a condition to be taken lightly, and it can significantly impact your daily life. The pain, discomfort, and potential limitations it brings can be overwhelming. In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the specifics of broad disc protrusion, exploring its causes, symptoms, and the latest advancements in treatment.
Understanding Broad Disc Protrusion: What It Is and How It Develops
Defining the Condition
A broad disc protrusion represents a specific type of spinal disc injury that occurs when the soft, gelatinous center of an intervertebral disc pushes outwards towards the spinal canal. This outward bulge, or protrusion, can press against nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, and other symptoms. Unlike a disc herniation, where the disc’s material breaks through the outer ring, a protrusion is more contained, but it can still cause significant discomfort.
Causes of Disc Protrusions
The development of a broad disc protrusion is often linked to a combination of factors:
- Age: As we age, the discs in our spines naturally lose their water content, becoming more susceptible to degeneration and protrusions.
- Repetitive Strain: Certain occupations that involve heavy lifting, repetitive movements, or prolonged sitting can put stress on the spinal discs, increasing the risk of protrusion.
- Trauma: Accidents, falls, or sudden, forceful movements can cause damage to the discs and contribute to protrusions.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to weakened or unstable discs, making them more likely to experience protrusions.
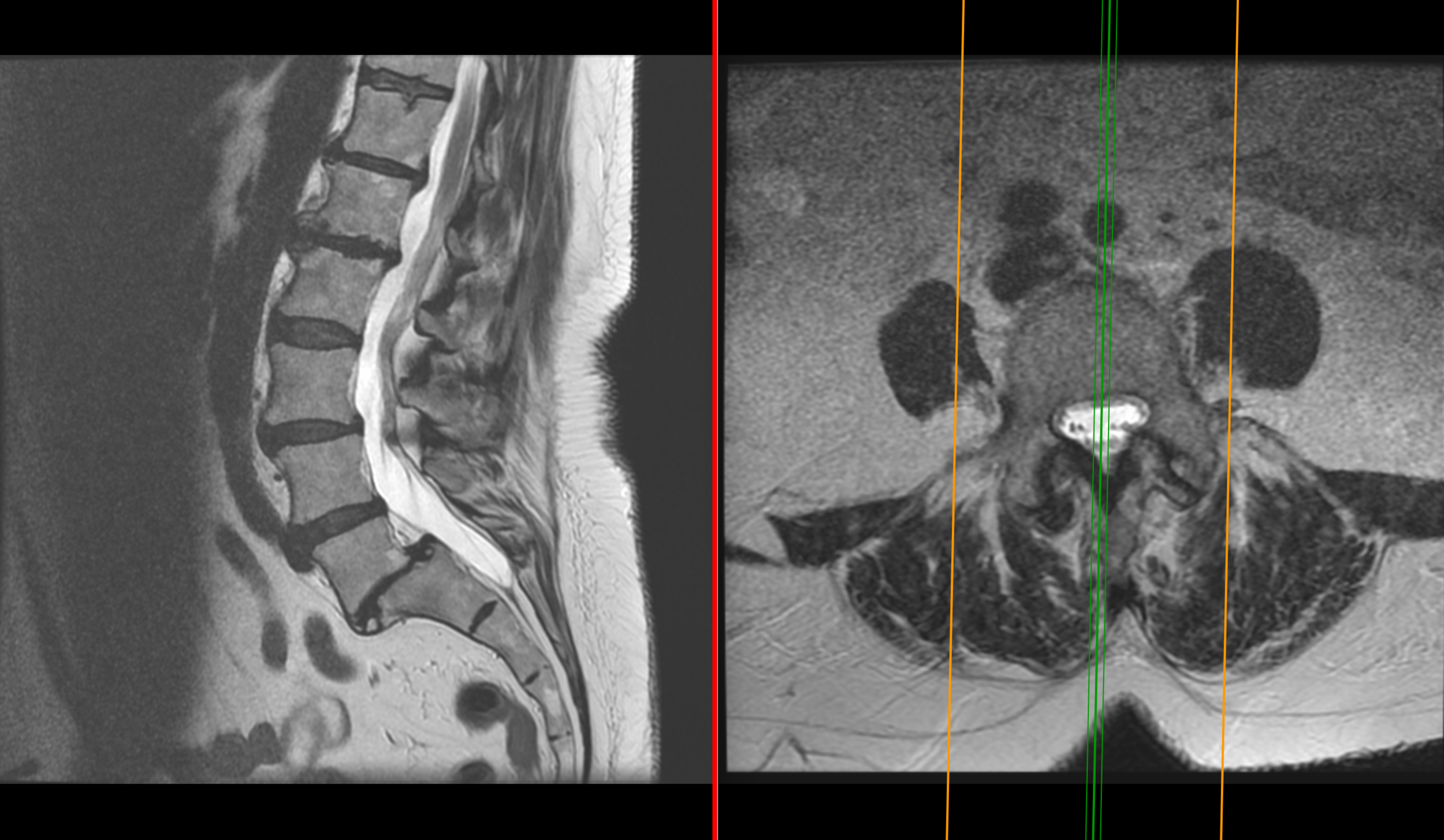
Image: www.aomsidiagnostics.com
Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs of a Broad Disc Protrusion
Knowing the common symptoms of a broad disc protrusion is crucial for early detection and timely management. While the experience can be varied depending on the location of the protrusion and the extent of nerve compression, here are some common indicators:
- Back Pain: Constant or intermittent pain in the lower back, often radiating to the buttocks or legs.
- Leg Pain: Often described as sciatica, this pain often shoots down one or both legs, potentially accompanied by numbness or tingling.
- Weakness: Difficulty controlling leg muscles, such as those responsible for lifting or walking, can be a symptom.
- Numbness or Tingling: A sensation of pins and needles or a loss of feeling in the legs or feet.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty bending or twisting the back can be a sign of a broad disc protrusion.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options: Getting the Right Care
Seeking Medical Expertise
If you’re experiencing any of the above symptoms, it’s essential to consult a medical professional, such as an orthopedic surgeon, spine specialist, or physiatrist. They can perform a comprehensive evaluation, including an examination of your physical symptoms, medical history, and imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans.
Treatment Strategies
The treatment approach for a broad disc protrusion is tailored to the severity of your condition and the underlying cause. Generally, the goal is to manage pain, reduce inflammation, and restore function. Here’s a breakdown of common treatment options:
- Conservative Treatments:
- Rest: Limited activity and avoidance of activities that worsen pain.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Exercises and stretches designed to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pressure on the spine.
- Heat or Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold to the affected area can provide temporary pain relief.
- Epidural steroid injections: Injecting corticosteroids into the space around the spinal nerves can reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Surgical Treatments:
- Discectomy: Surgery to remove the protruding disc material to reduce pressure on the nerves.
- Fusion: Joining two vertebrae together to stabilize the spine and prevent further movement.
Latest Trends and Advances: Exploring Breakthroughs in Disc Protrusion Treatment
The field of spinal care is constantly evolving, and exciting advancements are being made in the treatment of broad disc protrusions. Here are some notable trends shaping the future of this area:
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Advancements in minimally invasive surgical techniques allow for more precise targeting of the affected disc, leading to faster recovery times and fewer complications.
- Regenerative Medicine: Research is exploring the use of stem cells and other regenerative therapies to promote tissue repair and healing in the damaged disc.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Robotic systems offer surgeons enhanced precision and control during operations, potentially leading to improved outcomes.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: A growing emphasis on individualized care allows for the creation of tailored treatment plans based on each patient’s specific needs.
Tips and Expert Advice: Managing Your Disc Protrusion Effectively
While medical intervention is sometimes necessary, adopting proactive strategies to manage your broad disc protrusion can contribute significantly to your overall well-being.
Here are some expert tips to help you live a fulfilling life with a disc protrusion:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Extra weight puts stress on your spine, exacerbating disc protrusions.
- Practice Good Posture: Proper posture reduces strain on the lower back and can help prevent further disc problems.
- Strengthen Your Core Muscles: Strong core muscles provide stability for the spine and reduce the risk of further injuries.
- Learn Proper Lifting Techniques: Bend your knees and use your legs, not your back, to lift heavy objects.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, or cycling can strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and relieve pain. Discuss appropriate exercises with your medical professional to ensure they are safe for your condition.
Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Can a broad disc protrusion heal on its own?
A: In some cases, a broad disc protrusion can resolve without surgery. Rest, pain medication, and physical therapy can often be effective in managing symptoms and allowing the disc to heal. However, the recovery process can be lengthy, and the outcome depends on the severity of the protrusion and individual factors.
Q: Can a broad disc protrusion cause permanent nerve damage?
A: While prolonged compression of a nerve can lead to permanent damage, seeking timely treatment can usually prevent this from happening. Regular follow-up with your healthcare provider is important to monitor the situation and ensure proper management.
Q: How long does it take to recover from a broad disc protrusion?
A: The recovery time for a broad disc protrusion can vary significantly depending on the severity of the condition, treatment approach, and individual factors. It can take weeks to months for symptoms to improve, and a full recovery may take even longer. Be patient and follow your doctor’s instructions closely.
Broad Disc Protrusion
Conclusion: Embracing Hope and Taking Action
Broad disc protrusions can be a challenging condition, but with the right knowledge and resources, it’s possible to manage it effectively and live a fulfilling life. Understanding the condition, seeking professional guidance, and adopting proactive strategies can be instrumental in your journey toward recovery.
Are you experiencing symptoms related to a broad disc protrusion? Sharing your experiences and questions with the community can provide valuable support and insights. Let’s work together to understand and address this common spinal health issue.





