Imagine waking up one morning with a sharp, shooting pain in your back that radiates down your leg. You try to move, but the pain is so intense that you can barely stand. This is the reality for many people suffering from a superimposed central disc protrusion, a serious spinal condition that can significantly impact quality of life.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-99312322-56770c4a3df78ccc152764e1.jpg)
Image: www.verywellhealth.com
The pain associated with this condition is not just a nuisance; it can be debilitating, making it difficult to walk, stand, or even sit comfortably. This article will delve into the intricacies of superimposed central disc protrusion, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Superimposed Central Disc Protrusion: An In-Depth Look
A superimposed central disc protrusion occurs when the soft, gel-like center of an intervertebral disc bulges or protrudes outward, compressing the spinal nerves. Unlike other types of disc herniations, a superimposed central disc protrusion affects the center of the disc, putting pressure on the central spinal canal. This pressure can affect multiple nerve roots, potentially leading to more extensive pain and neurological symptoms.
The condition is often caused by repetitive strain or injury to the spine, particularly in individuals with poor posture or who engage in physically demanding activities. Age also plays a role as the discs in our spine gradually lose their ability to absorb shock and become more susceptible to degeneration.
Causes of Superimposed Central Disc Protrusion
The primary cause of a superimposed central disc protrusion is the deterioration of the intervertebral discs, which act as shock absorbers between the vertebrae. This deterioration can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Age: As we age, the discs naturally lose water content and elasticity, becoming more prone to tears and protrusions.
- Injury: A sudden, forceful impact to the spine, such as a car accident or a fall, can damage the discs and lead to a protrusion.
- Repetitive Strain: Repeated lifting, twisting, or bending can put excessive pressure on the discs, eventually causing them to protrude.
- Poor Posture: Slouching or maintaining an incorrect posture for prolonged periods can put strain on the spine, accelerating disc degeneration.
- Obesity: Excess weight can put extra strain on the spine, increasing the risk of disc herniation.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of a superimposed central disc protrusion is back pain, which can range from mild to severe. The pain typically worsens with movement or prolonged sitting. Other common symptoms include:
- Pain that radiates down the legs: This is known as sciatica and can be a debilitating symptom of a central disc protrusion.
- Numbness or tingling in the legs or feet: Nerve compression can cause these sensations.
- Weakness in the legs or feet: This can make it difficult to walk or stand.
- Bowel or bladder dysfunction: In severe cases, a central disc protrusion can press on the nerves that control bowel and bladder function, leading to incontinence or difficulty controlling these functions.
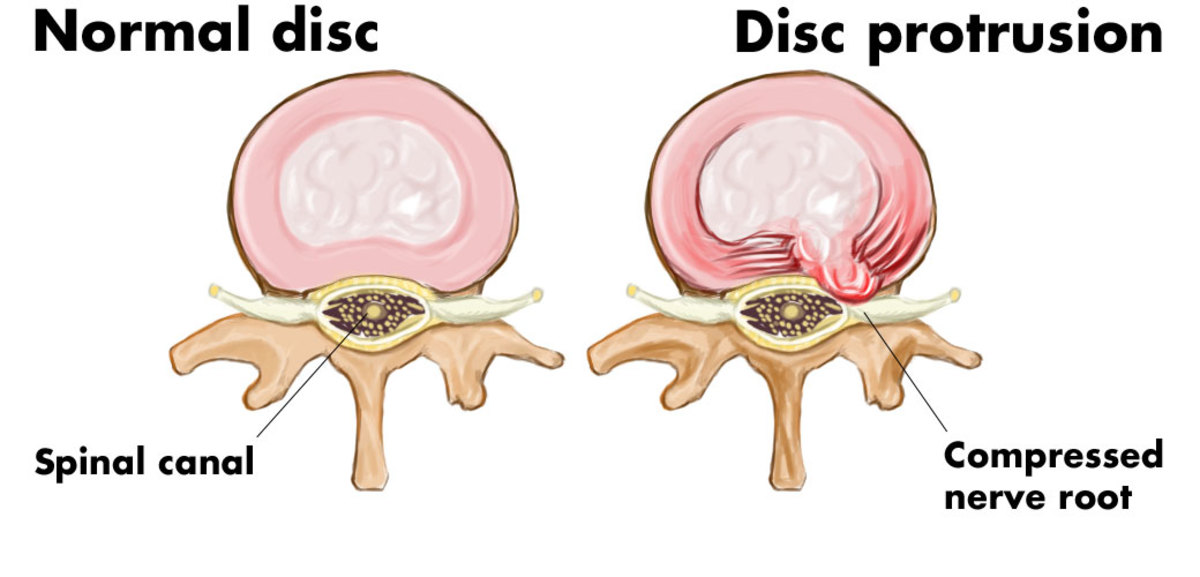
Image: healdove.com
Diagnosis
A thorough physical examination and medical history are usually sufficient to diagnose a superimposed central disc protrusion. The doctor will assess the patient’s pain, mobility, and neurological function. In addition to physical assessment, imaging tests, such as:
- X-rays: These tests can help to identify any bony abnormalities or misalignments in the spine.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This is the most accurate test for diagnosing a disc protrusion. MRI can visualize the discs and surrounding structures, revealing any herniations or nerve compression.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan: CT scans are primarily used to evaluate bony structures but can also show the spinal canal and disc herniations.
Treatment Options
Treatment for a superimposed central disc protrusion depends on the severity of the symptoms and the individual’s overall health.
Non-surgical Treatment Options
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises and stretches to improve your posture, strengthen your back muscles, and increase flexibility.
- Epidural steroid injections: These injections can be used to reduce pain and inflammation by delivering medication directly to the affected area.
Surgical Treatment Options
If non-surgical treatment options fail to relieve symptoms, surgery may be necessary. Common surgical procedures for a superimposed central disc protrusion include:
- Laminectomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of the bony arch of the vertebra (lamina) to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves and spinal cord.
- Discectomy: This is a surgical procedure to remove the herniated portion of the disc.
- Fusion: This procedure involves fusing two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine and prevent further disc herniation.
Trends and Developments
Recent years have witnessed significant advancements in the treatment of superimposed central disc protrusion, with a growing emphasis on minimally invasive procedures and personalized medicine. These trends are driven by the desire to minimize pain and recovery time, while maximizing patient outcomes.
One exciting development is the use of minimally invasive spine surgery techniques, which involve smaller incisions and less tissue damage. These techniques are often associated with faster recovery times and fewer complications. Another promising development is the use of advanced imaging technologies, such as 3D-guided surgery, which helps surgeons to visualize the target area with greater precision. This improved precision can lead to more effective treatment and reduced complications.
Tips and Expert Advice
Living with a superimposed central disc protrusion can be challenging, but there are steps you can take to manage your condition and improve your quality of life. Here are some expert tips.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly reduce the strain on your spine and mitigate pain.
- Practice Good Posture: Maintaining proper posture while standing, sitting, and moving can help to reduce pressure on your discs.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Strengthening your back muscles and improving flexibility can help to prevent further disc deterioration and maintain overall spine health.
- Avoid Lifting Heavy Objects: If you must lift, use proper lifting techniques to avoid putting extra strain on your spine.
- Seek Professional Help: If you experience back pain or any other symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about superimposed central disc protrusion:
- Q: How long does it take for a superimposed central disc protrusion to heal?
A: The healing time for a superimposed central disc protrusion varies depending on the severity of the condition and individual factors. In some cases, symptoms may resolve within a few weeks, while others may require several months or longer for improvement. - Q: Can a superimposed central disc protrusion be prevented?
A: While you cannot completely prevent disc herniation, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a healthy weight, good posture, and regular exercise, can significantly reduce your risk. - Q: What are the long-term effects of a superimposed central disc protrusion?
A: In many cases, symptoms of a superimposed central disc protrusion improve with treatment and lifestyle modifications. However, some individuals may experience persistent pain or neurological complications.
Superimposed Central Disc Protrusion
Conclusion
Superimposed central disc protrusion is a common spinal condition that can cause significant pain and discomfort. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition is critical for proper management and maintaining a good quality of life. While it is important to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, proactive lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and engaging in regular exercise can go a long way in preventing and managing this condition.
Have you or someone you know experienced a superimposed central disc protrusion? Share your experience in the comments section below, and let’s discuss this topic further.





